Mental fatigue level detection based on event related and visual evoked potentials features fusion in virtual indoor environment
- PMID: 31168331
- PMCID: PMC6520433
- DOI: 10.1007/s11571-019-09523-2
Mental fatigue level detection based on event related and visual evoked potentials features fusion in virtual indoor environment
Abstract
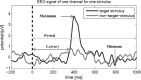
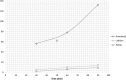
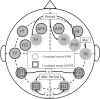
The purpose of this work is to set up a model that can estimate the mental fatigue of users based on the fusion of relevant features extracted from Positive 300 (P300) and steady state visual evoked potentials (SSVEP) measured by electroencephalogram. To this end, an experimental protocol describes the induction of P300, SSVEP and mental workload (which leads to mental fatigue by varying time-on-task) in different scenarios where environmental artifacts are controlled (obstacles number, obstacles velocities, ambient luminosity). Ten subjects took part in the experiment (with two suffering from cerebral palsy). Their mission is to navigate along a corridor from a starting point A to a goal point B where specific flickering stimuli are introduced to perform the P300 task. On the other hand, SSVEP task is elicited thanks to 10 Hz flickering lights. Correlated features are considered as inputs to fusion block which estimates mental workload. In order to deal with uncertainties and heterogeneity of P300 and SSVEP features, Dempster-Shafer (D-S) evidential reasoning is introduced. As the goal is to assess the reliability for the estimation of mental fatigue levels, D-S is compared to multi layer perception and linear discriminant analysis. The results show that D-S globally outperforms the other classifiers (although its performance significantly decreases between healthy and palsied groups). Finally we discuss the feasibility of such a fusion proposal in real life situation.
Keywords: BCI; Evidential reasoning; Mental fatigue; P300; SSVEP.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsAll procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Figures




References
-
- Cortese S, Ferrin M, Brandeis D, Buitelaar J, Daley D, Dittmann RW, Holtmann M, Santosh P, Stevenson J, Stringaris A, Zuddas A, Sonuga-Barke EJS. Cognitive training for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: meta-analysis of clinical and neuropsychological outcomes from randomized controlled trials. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2015;54(3):164–174. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2014.12.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crippa A, Maurits NM, Lorist MM, Roerdink JBTM. Visual computing in biology and medicine: graph averaging as a means to compare multichannel EEG coherence networks and its application to the study of mental fatigue and neurodegenerative disease. Comput Graph. 2011;35(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/j.cag.2010.12.008. - DOI
-
- Crowley K, Sliney A, Pitt I, Murphy D (2010) Evaluating a brain–computer interface to categorise human emotional response. In: Proceedings of the 2010 10th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies, ICALT ’10. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, pp 276–278
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

