SF3B1 mutation predicts unfavorable treatment-free survival in Chinese chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients
- PMID: 31168457
- PMCID: PMC6526254
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.03.63
SF3B1 mutation predicts unfavorable treatment-free survival in Chinese chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients
Abstract
Background: Splicing factor 3b subunit 1 (SF3B1), a splicing factor modulating RNA alternative splicing, is frequently mutated in multiple hematological malignancies including myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The clinical impact of SF3B1 mutation on CLL remains controversial especially for patients of Asian descent.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the frequency of SF3B1 mutation by Sanger sequencing in 399 newly diagnosed Chinese CLL patients.
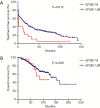
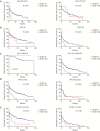
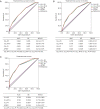
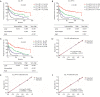
Results: SF3B1 mutation was detected in 5.5% (22/399) of the studied cohort with 59.1% of them being c.A2098G (p.K700E). SF3B1 mutation was common in patients with unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene, positive CD38 and positive ZAP-70. Survival analysis showed that SF3B1 mutation was associated with short treatment-free survival (TFS), but not overall survival (OS). We then developed 2 new risk models, named CLL-IPI-S and CLL-PI, according to the SF3B1 mutation status and CLL-international prognostic index (CLL-IPI); CLL-PI showed greater power to predict TFS than CLL-IPI in Chinese CLL patients.
Conclusions: Our data suggest a low incidence and adverse clinical significance of SF3B1 mutation in newly diagnosed Chinese CLL patients.
Keywords: Splicing factor 3b subunit 1 mutation (SF3B1 mutation); chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); prognosis; risk models.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Quijada-Alamo M, Hernandez-Sanchez M, Robledo C, et al. Next-generation sequencing and FISH studies reveal the appearance of gene mutations and chromosomal abnormalities in hematopoietic progenitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Hematol Oncol 2017;10:83. 10.1186/s13045-017-0450-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
