Epidemiology of Cardiac Amyloidosis-Associated Heart Failure Hospitalizations Among Fee-for-Service Medicare Beneficiaries in the United States
- PMID: 31170802
- PMCID: PMC6557425
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.118.005407
Epidemiology of Cardiac Amyloidosis-Associated Heart Failure Hospitalizations Among Fee-for-Service Medicare Beneficiaries in the United States
Abstract
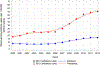
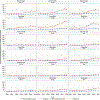
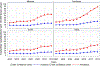
Background Cardiac amyloidosis is a substantially underdiagnosed disease, and contemporary estimates of the epidemiology of amyloidosis are lacking. This study aims to determine the incidence and prevalence of cardiac amyloidosis among Medicare beneficiaries from 2000 to 2012. Methods and Results Medicare beneficiaries were counted in the prevalence cohort in each year they had (1) ≥1 principal or secondary International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision code for amyloidosis and (2) ≥1 principal or secondary International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision code for heart failure or cardiomyopathy within 2 years after the systemic amyloidosis code. A beneficiary was counted in the incidence cohort only during the first year in which they met criteria. Primary outcomes included the prevalence and incidence of hospitalizations for cardiac amyloidosis. There were 4746 incident cases of cardiac amyloidosis in 2012 and 15 737 prevalent cases in 2012. There was also a significant increase in the prevalence rate (8 to 17 per 100 000 person-years) and incidence rate (18 to 55 per 100 000 person-years) from 2000 to 2012, most notable after 2006. Incidence and prevalence increased substantially more among men, the elderly, and in blacks. Conclusions The incidence and prevalence rates of cardiac amyloidosis are higher than previously thought. The incidence and prevalence rates of cardiac amyloidosis among hospitalized patients have increased since 2000, particularly among specific patient subgroups and after 2006, suggesting improved amyloidosis awareness and higher diagnostic rates with noninvasive imaging. In light of these trends, cardiac amyloidosis should be considered during the initial work up of patients ≥65 years old hospitalized with heart failure.
Keywords: Medicare; amyloidosis; heart failure; incidence; prevalence.
Figures


Comment in
-
Cardiac Amyloidosis A Rare Disease in Older Adults Hospitalized for Heart Failure?Circ Heart Fail. 2019 Jun;12(6):e006169. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.119.006169. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Circ Heart Fail. 2019. PMID: 31172792 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dubrey SW, Cha K, Anderson J, Chamarthi B, Reisinger J, Skinner M and Falk RH. The clinical features of immunoglobulin light-chain (AL) amyloidosis with heart involvement. QJM : monthly journal of the Association of Physicians 1998;91:141–57. - PubMed
-
- Muchtar E, Gertz MA, Kumar SK, Lacy MQ, Dingli D, Buadi FK, Grogan M, Hayman SR, Kapoor P, Leung N, Fonder A, Hobbs M, Hwa YL, Gonsalves W, Warsame R, Kourelis TV, Russell S, Lust JA, Lin Y, Go RS, Zeldenrust S, Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV and Dispenzieri A. Improved outcomes for newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis between 2000 and 2014: cracking the glass ceiling of early death. Blood 2017;129:2111–2119. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

