Loop-mediated isothermal amplification-fluorescent loop primer assay for the genotyping of a single nucleotide polymorphism at position 2254 in the viral DNA polymerase gene of equid alphaherpesvirus 1
- PMID: 31170890
- PMCID: PMC6857012
- DOI: 10.1177/1040638719856404
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification-fluorescent loop primer assay for the genotyping of a single nucleotide polymorphism at position 2254 in the viral DNA polymerase gene of equid alphaherpesvirus 1
Abstract
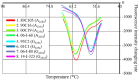
We developed a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)-fluorescent loop primer (FLP) assay for genotyping the A/G2254 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the viral DNA polymerase gene of species Equid alphaherpesvirus 1 (EHV-1), which is associated with the neuropathogenic potential of this virus. In addition to the use of regular LAMP primers to amplify the target region, a 5'-FAM-labeled backward loop primer (FLB) and 3'-dabcyl-labeled quencher probe (QP) were designed for annealing curve analysis of the amplification product. The QP, which contacts the FLB, is located at the SNP site and has the A2254 allele. LAMP reactions were performed at 63°C for 40 min, and the subsequent annealing curve analyses were accomplished within 20 min. The LAMP-FLP assay could clearly differentiate A2254 and G2254 genotypes according to the difference in the annealing temperature of the QP between the 2 genotypes. Good agreement between the LAMP-FLP and the real-time PCR for genotyping of this SNP was observed in the detection of EHV-1 in equine clinical samples. The newly developed assay is a simple and rapid method for detecting and differentiating EHV-1 strains with A2254 and G2254 polymorphisms and would be suitable for clinical use.
Keywords: equid herpesvirus 1; genotyping techniques; polymorphism; single nucleotide.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel PCR protocol for detection and differentiation of neuropathogenic and non-neuropathogenic equid alphaherpesvirus 1.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2019 Sep;31(5):696-703. doi: 10.1177/1040638719871975. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2019. PMID: 31477001 Free PMC article.
-
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for detection of Equid herpesvirus 1 and 4 and differentiating a gene-deleted candidate vaccine strain from wild-type Equid herpesvirus 1 strains.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2010 Jan;22(1):30-6. doi: 10.1177/104063871002200105. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2010. PMID: 20093679
-
Detection and genotyping of equid herpesvirus 1 in Uruguay.Rev Sci Tech. 2017 Dec;36(3):799-806. doi: 10.20506/rst.36.3.2715. Rev Sci Tech. 2017. PMID: 30160700
-
AS-LAMP: A New and Alternative Method for Genotyping.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2020 Jan-Mar;12(1):2-8. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32153732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Mutation Detection Using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification.ACS Omega. 2021 Jan 28;6(5):3463-3469. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06093. eCollection 2021 Feb 9. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33585732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosing the drug resistance signature in Plasmodium falciparum: a review from contemporary methods to novel approaches.J Parasit Dis. 2021 Sep;45(3):869-876. doi: 10.1007/s12639-020-01333-2. Epub 2021 Jan 7. J Parasit Dis. 2021. PMID: 34475670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Super-assembly of integrated gold magnetic assay with loop-mediated isothermal amplification for point-of-care testing.Nano Res. 2023;16(1):1242-1251. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4692-9. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Nano Res. 2023. PMID: 35966151 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time fluorometric and end-point colorimetric isothermal assays for detection of equine pathogens C. psittaci and equine herpes virus 1: validation, comparison and application at the point of care.BMC Vet Res. 2021 Aug 19;17(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02986-8. BMC Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34412635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen GP. Risk factors for development of neurologic disease after experimental exposure to equine herpesvirus-1 in horses. Am J Vet Res 2008;69:1595–1600. - PubMed
-
- Allen GP, et al. Equid herpesvirus 1 and equid herpesvirus 4 infections. In: Coetzer J AW, et al., eds. Infectious Diseases of Livestock. Cape Town: Oxford University Press, 2004:829–859.
-
- Goehring LS, et al. Equine herpesvirus type 1-associated myeloencephalopathy in The Netherlands: a four-year retrospective study (1999–2003). J Vet Intern Med 2006;20:601–607. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources