Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) mediates hepatic stellate cell activation via ALK5/Smad signalling
- PMID: 31171625
- PMCID: PMC6842044
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317872
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) mediates hepatic stellate cell activation via ALK5/Smad signalling
Abstract
Objective: Although glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a member of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily, its function in liver fibrosis has rarely been studied. Here, we investigated the role of GDNF in hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and liver fibrosis in humans and mice.
Design: GDNF expression was examined in liver biopsies and sera from patients with liver fibrosis. The functional role of GDNF in liver fibrosis was examined in mice with adenoviral delivery of the GDNF gene, GDNF sgRNA CRISPR/Cas9 and the administration of GDNF-blocking antibodies. GDNF was examined on HSC activation using human and mouse primary HSCs. The binding of activin receptor-like kinase 5 (ALK5) to GDNF was determined using surface plasmon resonance (SPR), molecular docking, mutagenesis and co-immunoprecipitation.
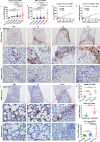
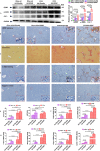
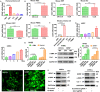
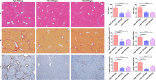
Results: GDNF mRNA and protein levels are significantly upregulated in patients with stage F4 fibrosis. Serum GDNF content correlates positively with α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and Col1A1 mRNA in human fibrotic livers. Mice with overexpressed GDNF display aggravated liver fibrosis, while mice with silenced GDNF expression or signalling inhibition by GDNF-blocking antibodies have reduced fibrosis and HSC activation. GDNF is confined mainly to HSCs and contributes to HSC activation through ALK5 at His39 and Asp76 and through downstream signalling via Smad2/3, but not through GDNF family receptor alpha-1 (GFRα1). GDNF, ALK5 and α-SMA colocalise in human and mouse HSCs, as demonstrated by confocal microscopy.
Conclusions: GDNF promotes HSC activation and liver fibrosis through ALK5/Smad signalling. Inhibition of GDNF could be a novel therapeutic strategy to combat liver fibrosis.
Keywords: chronic liver disease; hepatic fibrosis; hepatic stellate cell.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Lai KKY, Kweon SM, Chi F, et al. . Stearoyl-CoA desaturase promotes liver fibrosis and tumor development in mice via a wnt positive-signaling loop by stabilization of low-density lipoprotein-receptor-related proteins 5 and 6. Gastroenterology 2017;152:1477–91. 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.01.021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
