A wave of Foxp3+ regulatory T cell accumulation in the neonatal liver plays unique roles in maintaining self-tolerance
- PMID: 31171863
- PMCID: PMC7193579
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-019-0246-9
A wave of Foxp3+ regulatory T cell accumulation in the neonatal liver plays unique roles in maintaining self-tolerance
Abstract
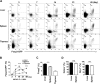
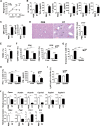
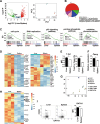
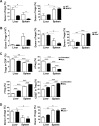
Newborn animals require tightly regulated local and systemic immune environments to govern the development and maturation of multiple organs/tissues even though the immune system itself is far from mature during the neonatal period. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are essential for maintaining immune tolerance/homeostasis and modulating inflammatory responses. The features of Tregs in the neonatal liver under steady-state conditions are not well understood. The present study aimed to investigate the phenotype, functions, and significance of neonatal Tregs in the liver. We found a wave of thymus-derived Treg influx into the liver during 1-2 weeks of age. Depletion of these Tregs between days 7 and 11 after birth rapidly resulted in Th1-type liver inflammation and metabolic disorder. More Tregs in the neonatal liver than in the spleen underwent MHC II-dependent activation and proliferation, and the liver Tregs acquired stronger suppressive functions. The transcriptomic profile of these neonatal liver Tregs showed elevated expression of PPARγ and T-bet and features of Tregs that utilize lipid metabolic machinery and are capable of regulating Th1 responses. The accumulation of Tregs with unique features in the neonatal liver is critical to ensure self-tolerance and liver maturation.
Keywords: Foxp3; Neonatal period,; Th1-type inflammation; Treg cells; liver.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Grijalva J, Vakili K. Neonatal liver physiology. Semin Pedia. Surg. 2013;22:185–189. - PubMed
-
- Nakagaki B. N., et al. Immune and metabolic shifts during neonatal development reprogram liver identity and function. J. Hepatol.69, 1294–1307 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Weaver LT, Laker MF, Nelson R, Lucas A. Milk feeding and changes in intestinal permeability and morphology in the newborn. J. Pedia. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1987;6:351–358. - PubMed
-
- Prandota J. Possible pathomechanisms of sudden infant death syndrome: key role of chronic hypoxia, infection/inflammation states, cytokine irregularities, and metabolic trauma in genetically predisposed infants. Am. J. Ther. 2004;11:517–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

