Yeast AP-1 like transcription factors (Yap) and stress response: a current overview
- PMID: 31172012
- PMCID: PMC6545440
- DOI: 10.15698/mic2019.06.679
Yeast AP-1 like transcription factors (Yap) and stress response: a current overview
Abstract
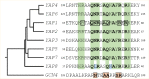
Yeast adaptation to stress has been extensively studied. It involves large reprogramming of genome expression operated by many, more or less specific, transcription factors. Here, we review our current knowledge on the function of the eight Yap transcription factors (Yap1 to Yap8) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which were shown to be involved in various stress responses. More precisely, Yap1 is activated under oxidative stress, Yap2/Cad1 under cadmium, Yap4/Cin5 and Yap6 under osmotic shock, Yap5 under iron overload and Yap8/Arr1 by arsenic compounds. Yap3 and Yap7 seem to be involved in hydroquinone and nitrosative stresses, respectively. The data presented in this article illustrate how much knowledge on the function of these Yap transcription factors is advanced. The evolution of the Yap family and its roles in various pathogenic and non-pathogenic fungal species is discussed in the last section.
Keywords: Yap factors; bZIP; cis-elements; stress; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Yap, a novel family of eight bZIP proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with distinct biological functions.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Dec;17(12):6982-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.12.6982. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9372930 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Yap1 towards Saccharomyces cerevisiae adaptation to arsenic-mediated oxidative stress.Biochem J. 2008 Sep 1;414(2):301-11. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071537. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18439143
-
The ancillary N-terminal region of the yeast AP-1 transcription factor Yap8 contributes to its DNA binding specificity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 4;48(10):5426-5441. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa316. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32356892 Free PMC article.
-
The Yap family and its role in stress response.Yeast. 2010 May;27(5):245-58. doi: 10.1002/yea.1752. Yeast. 2010. PMID: 20148391 Review.
-
Redox control of AP-1-like factors in yeast and beyond.Oncogene. 2001 Apr 30;20(19):2336-46. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204384. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11402331 Review.
Cited by
-
Manganese Stress Tolerance Depends on Yap1 and Stress-Activated MAP Kinases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 11;23(24):15706. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415706. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555348 Free PMC article.
-
The fungal CCAAT-binding complex and HapX display highly variable but evolutionary conserved synergetic promoter-specific DNA recognition.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 17;48(7):3567-3590. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa109. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32086516 Free PMC article.
-
Fused oxazepine-naphthoquinones as novel cytotoxic agents with diverse modes of action in yeast.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 10;10(24):e41105. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41105. eCollection 2024 Dec 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39759308 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor control of virulence in phytopathogenic fungi.Mol Plant Pathol. 2021 Jul;22(7):858-881. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13056. Epub 2021 May 11. Mol Plant Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33973705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increasing NADPH impairs fungal H2O2 resistance by perturbing transcriptional regulation of peroxiredoxin.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022 Jan 3;9(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40643-021-00489-w. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022. PMID: 38647831 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
