Development of an enzyme‑linked immunosorbent assay for camptothecin
- PMID: 31173229
- PMCID: PMC6625201
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10342
Development of an enzyme‑linked immunosorbent assay for camptothecin
Abstract
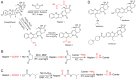
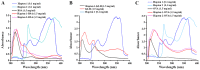
The use of camptothecin and its analogues has increased in clinical settings and in agriculture. Therefore, camptothecins and their derivatives, metabolites and degradation products are frequently found in the environment. Therefore, it is important to develop an ELISA for the quantification of camptothecins in human plasma, plants, animal tissues and other matrices. The present study developed a novel competitive indirect ELISA for camptothecin using a monoclonal antibody (MAb). In total, two haptens and various carrier proteins were tested to select the most suitable immunogen for the production of MAbs against camptothecin. Hapten 1 conjugated with keyhole limpet hemocyanin was selected for the preparation of MAb 5A3, and was used to establish a competitive indirect ELISA for camptothecin. A total of three derivatives of camptothecin used in clinical practice were examined. Topotecan showed an IC50 value of 0.68 µg/ml with a detection limit of 0.19 µg/ml, belotecan showed an IC50 value of 0.87 µg/ml with a detection limit of 0.22 µg/ml and irinotecan showed an IC50 value of 2.85 µg/ml with a detection limit of 0.47 µg/ml. The cross‑reactivity results suggested that the assay developed in the present study possessed a high sensitivity to camptothecin. Therefore, this immunoassay technique may be suitable for monitoring the levels of camptothecin in compound analysis, clinical applications, and analyses of food and environmental samples.
Figures
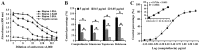
Similar articles
-
Monoclonal antibody production and the development of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for screening T-2 toxin in milk.Toxicon. 2018 Dec 15;156:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2018.10.307. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Toxicon. 2018. PMID: 30391579
-
Development of monoclonal antibodies against pirimiphos-methyl and their application to IC-ELISA.J Agric Food Chem. 2006 Jun 28;54(13):4551-6. doi: 10.1021/jf0606196. J Agric Food Chem. 2006. PMID: 16786997
-
Hapten synthesis, monoclonal antibody production and development of a competitive indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for erythromycin in milk.Food Chem. 2015 Mar 15;171:98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.104. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25308648
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative/qualitative analysis of plant secondary metabolites.J Nat Med. 2018 Jan;72(1):32-42. doi: 10.1007/s11418-017-1144-z. Epub 2017 Nov 21. J Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 29164507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid immunoassays for the detection of quinoxalines and their metabolites residues in animal-derived foods: A review.Food Chem. 2024 Jun 15;443:138539. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138539. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38320375 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in Immunoassays of Toxic Alkaloids in Plant-Derived Medicines: A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;14(3):165. doi: 10.3390/toxins14030165. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35324662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of anti-SN38 antibody for loading efficacy and therapeutic monitoring of SN38-containing therapeutics.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 18;10(12):e33232. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33232. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39021912 Free PMC article.
-
Growth inhibition of Spodoptera frugiperda larvae by camptothecin correlates with alteration of the structures and gene expression profiles of the midgut.BMC Genomics. 2021 May 26;22(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07726-8. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34039281 Free PMC article.
-
Biomacromolecule-Assisted Screening for Reaction Discovery and Catalyst Optimization.Chem Rev. 2022 Aug 24;122(16):13800-13880. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00213. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35904776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wall ME, Wani MC, Cook CE, Palmer KH, McPhail AT, Sim GA. Plant antitumor agents I. The isolation and structure of camptothecin, a novel alkaloidal leukemia and tumor inhibitor from Camptotheca acuminata. J Am Chem Soc. 1966;88:3888–3890. doi: 10.1021/ja00968a057. - DOI
-
- Jensen NF, Agama K, Roy A, Smith DH, Pfster TD, Romer MU, Zhang HL, Doroshow JH, Knudsen BR, Stenvang J, et al. Characterization of DNA topoisomerase I in three SN-38 resistant human colon cancer cell lines reveals a new pair of resistance-associated mutations. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016;35:56. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0335-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hsiang YH, Hertzberg R, Hecht S, Liu LF. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:14873–14878. - PubMed

