Efficacy of two telemonitoring systems to improve glycaemic control during basal insulin initiation in patients with type 2 diabetes: The TeleDiab-2 randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 31173451
- PMCID: PMC6771866
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13806
Efficacy of two telemonitoring systems to improve glycaemic control during basal insulin initiation in patients with type 2 diabetes: The TeleDiab-2 randomized controlled trial
Abstract
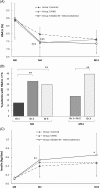
TeleDiab-2 was a 13-month randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of two telemonitoring systems to optimize basal insulin (BI) initiation in subjects with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes (HbA1c, 7.5%-10%). A total of 191 participants (mean age 58.7 years, mean HbA1c 8.9%) were randomized into three groups: group 1(G1, standard care, n = 63), group 2 (G2, interactive voice response system, n = 64) and group 3 (G3, Diabeo-BI app software, n = 64). The two telemonitoring systems proposed daily adjustments of BI doses, in order to facilitate the achievement of fasting blood glucose (FBG) values targeted at ~100 mg/dL. At 4 months follow-up, HbA1c reduction was significantly higher in the telemonitoring groups (G2: -1.44% and G3: -1.48% vs. G1: -0.92%; P < 0.002). Moreover, target FBG was reached by twice as many patients in the telemonitoring groups as in the control group, and insulin doses were also titrated to higher levels. No severe hypoglycaemia was observed in the telemonitoring groups and mild hypoglycaemia frequency was similar in all groups. In conclusion, both telemonitoring systems improved glycaemic control to a similar extent, without increasing hypoglycaemic episodes.
Keywords: basal insulin; glycaemic control; insulin therapy; randomized trial; type 2 diabetes.
© 2019 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
S.F., A.D., C.R. and G.C. are employees of CERITD. G.O. is an employee of Voluntis. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests. CERITD funded the study. Novo Nordisk provided an unrestricted grant.
Figures

References
-
- Bouée S, Avignon A, Halimi S. Diabète de type 2: pratiques d'intensification thérapeutique chez les médecins généralistes en France en 2008–2009. Bulletin Epidémiologique Hebdomadaire. 2010;42–43:436‐440.
-
- Yki‐Järvinen H, Kauppinen‐Mäkelin R, Tiikkainen M, et al. Insulin glargine or NPH combined with metformin in type 2 diabetes: the LANMET study. Diabetologia. 2006;49:442‐451. - PubMed
-
- Charpentier G, Benhamou P‐Y, Dardari D, et al. The Diabeo software enabling individualized insulin dose adjustments combined with telemedicine support improves HbA1c in poorly controlled type 1 diabetic patients: a 6‐month, randomized, open‐label, parallel‐group, multicenter trial (TeleDiab‐1 study). Diabetes Care. 2011;34:533‐539. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

