Real-world treatment patterns and adverse events in metastatic renal cell carcinoma from a large US claims database
- PMID: 31174493
- PMCID: PMC6555983
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5716-z
Real-world treatment patterns and adverse events in metastatic renal cell carcinoma from a large US claims database
Abstract
Background: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), tyrosine kinase (TK) and mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR) inhibitors are common first-line (1 L) treatments for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Despite treatment availability, the 5-year survival rate in patients diagnosed at the metastatic stage is only ≈ 10%. To gain contemporary insights into RCC treatment trends that may inform clinical, scientific and payer considerations, treatment patterns and adverse events (AEs) associated with 1 L therapy were examined in a retrospective, longitudinal, population-based, observational study of patients with mRCC.
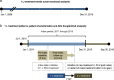
Methods: US administrative claims data (Truven Health MarketScan Commercial Databases) were used to assess trends in 1 L treatment initiation in mRCC (2006-2015) and characterize patterns of individual 1 L treatments, baseline characteristics, comorbidities and treatment-related AEs from 2011 through 2015. Outcomes were evaluated by drug class and route of administration.
Results: Ten-year trend analysis (n = 4270) showed that TK/VEGF-directed therapy rapidly became more common than mTOR-directed therapy, and oral treatments were favored over intravenous (IV) treatments. Overall, 1992 eligible patients initiated 1 L treatment for mRCC from 2011 through 2015: 1752 (88%) received TK/VEGF-directed agents and 233 (12%) received mTOR-directed agents; 1674 (84%) received oral treatments, and 318 (16%) received IV treatments. The most common 1 L treatment was sunitinib (n = 849), followed by pazopanib (n = 631), temsirolimus (n = 157) and bevacizumab (n = 154). Patient characteristics and comorbidities, including age, diabetes and congestive heart failure, were independent predictors of 1 L mRCC treatment choice. The three most common potentially 1 L treatment-related AEs were nausea/vomiting (128.2 per 100 patient-years [PY]), hypertension (69 per 100 PY) and renal insufficiency (44.6 per 100 PY). A wide variety of agents were used as second-line (2 L) therapy. Substantial latency of onset was observed for several potentially treatment-related toxicities in patients treated with TK/VEGF- or mTOR-directed agents.
Conclusions: In the US, 1 L TK/VEGF inhibitor uptake in recent years appears largely in line with national approvals and guidelines, with varied 2 L agent use. Although retrospective evaluation of claims data cannot assess underlying causality, insights from these real-world RCC treatment and AE patterns will be useful in informing medical and payer decisions.
Keywords: Administrative claims; Adverse events; Renal cell carcinoma; Targeted therapy; Treatment patterns.
Conflict of interest statement
SP reports honoraria and a consulting/advisory role with Novartis, Astellas, Aveo, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Exelixis, Ipsen, Myriad Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer and Roche/Genentech and honoraria and research funding from Medivation. AS is employed by Genesis Research and reports a consulting/advisory role with Roche/Genentech. SKM, SW and SO are employees of Genentech, Inc. and own Roche stock. DG reports consulting/advisory roles with Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Clovis, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Innocrin, Janssen, Myovant, Pfizer and Sanofi and received research funding from Astellas, Bayer, Innocrin, Janssen, Novartis and Pfizer. HW is a former employee of Roche/Genentech. RV was a paid intern at Roche/Genentech at the time of the study. JG declares that he has no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Role of immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell cancer: past, present and future.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Dec;7(Suppl 8):S349. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.95. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 32016067 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Patterns of Care in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Among a U.S. Payer Population with Commercial or Medicare Advantage Membership.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016 Mar;22(3):219-26. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2016.22.3.219. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27003551 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment patterns in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a retrospective review of medical records from US community oncology practices.Curr Med Res Opin. 2014 Oct;30(10):2041-50. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2014.938730. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014. PMID: 24983741
-
Real-World Axitinib Use in the United States: A Retrospective Study Using Linked Datasets.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016 Jun;22(6):723-732u. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2016.22.6.723. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27231799 Free PMC article.
-
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary Site (CUP) With Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma (mRCC) Histologic and Immunohistochemical Characteristics (CUP-mRCC): Results From Consecutive Patients Treated With Targeted Therapy and Review of Literature.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2019 Feb;17(1):e32-e37. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30268423 Review.
-
Targeted treatment for metastatic renal cell carcinoma and immune regulation.J BUON. 2010 Apr-Jun;15(2):235-40. J BUON. 2010. PMID: 20658715 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges for the evaluation of digital health solutions-A call for innovative evidence generation approaches.NPJ Digit Med. 2020 Aug 27;3:110. doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-00314-2. eCollection 2020. NPJ Digit Med. 2020. PMID: 32904379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Disease and Other Competing Causes of Death in Older Kidney Cancer Patients.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jan 14;26(1):25277. doi: 10.31083/RCM25277. eCollection 2025 Jan. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 39867178 Free PMC article.
-
The microbiota and renal cell carcinoma.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Apr;47(2):397-413. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00876-9. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 37878209 Review.
-
Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastasis to the Penis: A Case Report and Literature Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Mar 29;60(4):554. doi: 10.3390/medicina60040554. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38674200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical-radiomic model in advanced kidney cancer predicts response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Oncol Lett. 2022 Oct 26;24(6):446. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13566. eCollection 2022 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36420068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Cancer Institute. SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Kidney and Renal Pelvis Cancer. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/kidrp.html. Accessed 3 Feb 2019.
-
- American Cancer Society. Survival rates for kidney cancer by stage. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/kidney-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/.... Accessed 3 Feb 2019.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

