Comparison of the long-term follow-up and perioperative outcomes of partial nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy for 4 cm to 7 cm renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31174522
- PMCID: PMC6554915
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-019-0480-6
Comparison of the long-term follow-up and perioperative outcomes of partial nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy for 4 cm to 7 cm renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of partial nephrectomy (PN) for T1b renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is controversial. The oncological outcomes, the change in postoperative renal function and the perioperative complications are unclear.
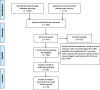
Methods: We searched PUBMED, EMBASE and the Cochrane Central Register for studies from March 1998 to March 2018 for studies comparing PN to radical nephrectomy (RN) for the treatment of T1b RCC. After data extraction and quality assessment, we used RevMan 5.2 to pool the data. Then, we used Stata 12.0 to perform sensitivity analyses and meta-regression. We used the GRADE profiler to evaluate the evidence according to the GRADE approach.
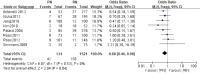
Results: A total of 16 studies involving 33,117 patients were included in our meta-analysis. No significant difference was found in the 5-year overall survival (OS), 10-year OS, 5-year recurrence-free survival (RFS) and 10-year RFS. The 5-year cancer-special survival (CSS) and 10-year CSS were better in RN compared to PN, respectively, at RR = 1.02, P < 0.05 and RR = 1.04, P < 0.05. PN was better than RN in the preservation of renal function (WMD = -9.15, 95% CI: - 10.30 to - 7.99, P < 0.05). The confidence level grading of the evidence was moderate for 5-year OS, 10-year OS, 5-year CSS, 10-year CSS, 5-year RFS, 10-year RFS, tumor recurrence, decline in eGFR, and postoperative complications.
Conclusions: PN may provide comparable outcomes in terms of RFS & OS, and better renal function preservation although CSS was worse.
Keywords: Cancer special survival; Overall survival; Partial nephrectomy; Radical nephrectomy; Recurrence-free survival; Renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

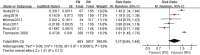
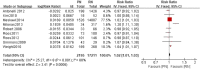


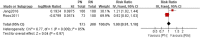

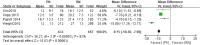
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

