The cargo adaptor proteins RILPL2 and melanophilin co-regulate myosin-5a motor activity
- PMID: 31175157
- PMCID: PMC6643029
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007384
The cargo adaptor proteins RILPL2 and melanophilin co-regulate myosin-5a motor activity
Abstract
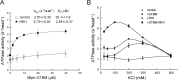
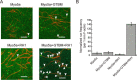
Vertebrate myosin-5a is an ATP-utilizing processive motor associated with the actin network and responsible for the transport and localization of several vesicle cargoes. To transport cargo efficiently and prevent futile ATP hydrolysis, myosin-5a motor function must be tightly regulated. The globular tail domain (GTD) of myosin-5a not only functions as the inhibitory domain but also serves as the binding site for a number of cargo adaptor proteins, including melanophilin (Mlph) and Rab-interacting lysosomal protein-like 2 (RILPL2). In this study, using various biochemical approaches, including ATPase, single-molecule motility, GST pulldown assays, and analytical ultracentrifugation, we demonstrate that the binding of both Mlph and RILPL2 to the GTD of myosin-5a is required for the activation of myosin-5a motor function under physiological ionic conditions. We also found that this activation is regulated by the small GTPase Rab36, a binding partner of RILPL2. In summary, our results indicate that RILPL2 is required for Mlph-mediated activation of Myo5a motor activity under physiological conditions and that Rab36 promotes this activation. We propose that Rab36 stimulates RILPL2 to interact with the myosin-5a GTD; this interaction then induces exposure of the Mlph-binding site in the GTD, enabling Mlph to interact with the GTD and activate myosin-5a motor activity.
Keywords: Rab; Rab36; actin; allosteric regulation; melanophilin; melanosome; molecular motor; myosin; myosin-5a; organelle; small GTPase; vesicle transport.
© 2019 Cao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

