How FtsEX localizes to the Z ring and interacts with FtsA to regulate cell division
- PMID: 31175681
- PMCID: PMC6831102
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.14324
How FtsEX localizes to the Z ring and interacts with FtsA to regulate cell division
Abstract
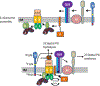
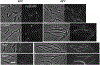
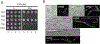
In Escherichia coli, FtsEX, a member of the ABC transporter superfamily, is involved in regulating the assembly and activation of the divisome to couple cell wall synthesis to cell wall hydrolysis at the septum. Genetic studies indicate FtsEX acts on FtsA to begin the recruitment of the downstream division proteins but blocks septal PG synthesis until a signal is received that divisome assembly is complete. However, the details of how FtsEX localizes to the Z ring and how it interacts with FtsA are not clear. Our results show that recruitment of FtsE and FtsX is codependent and suggest that the FtsEX complex is recruited through FtsE interacting with the conserved tail of FtsZ (CCTP), thus adding FtsEX to a growing list of proteins that interacts with the CCTP of FtsZ. Furthermore, we find that the N-terminus of FtsX is not required for FtsEX localization to the Z ring but is required for its functions in cell division indicating that it interacts with FtsA. Taken together, these results suggest that FtsEX first interacts with FtsZ to localize to the Z ring and then interacts with FtsA to promote divisome assembly and regulate septal PG synthesis.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




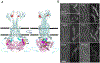
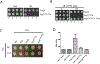
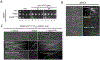
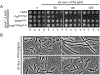
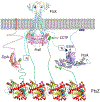
References
-
- Aarsman ME, Piette A, Fraipont C, Vinkenvleugel TM, Nguyen-Disteche M & den Blaauwen T, (2005) Maturation of the Escherichia coli divisome occurs in two steps. Molecular microbiology 55: 1631–1645. - PubMed
-
- Addinall SG, Cao C & Lutkenhaus J, (1997) FtsN, a late recruit to the septum in Escherichia coli. Molecular microbiology 25: 303–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

