Regional differences in white matter integrity in stimulant use disorders: A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging studies
- PMID: 31176066
- PMCID: PMC6660908
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.03.023
Regional differences in white matter integrity in stimulant use disorders: A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging studies
Abstract
Background: Converging lines of evidence from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies reveal significant alterations in white matter (WM) microstructure in the prefrontal cortex of chronic stimulant users compared to controls, suggesting compromised axonal microstructure and/or myelin.
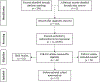
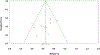
Methods: A meta-analysis of DTI-based WM integrity was conducted for white matter regions across the corpus callosum and association fibers. Articles were sourced and selected using PRISMA guidelines for systematic review and meta-analysis. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were determined by the authors in order to best capture WM integrity among individuals with primary stimulant use in comparison to healthy control subjects.
Results: Eleven studies that focused on region-of-interest (ROI)-based analysis of WM integrity were extracted from an initial pool of 113 independent studies. Analysis across ROIs indicated significantly lower fractional anisotropy (FA) values in stimulant use groups compared to controls with a small to moderate overall effect (Hedges' g = -0.37, 95% CI [-0.54, -0.20]). Eigenvalues were also analyzed, revealing a significant effect for radial diffusivity (RD; Hedges' g = 0.24, 95% CI [0.01, 0.47]) but not axial diffusivity (AD; Hedges' g = 0.05, 95% CI [-0.20, 0.29]) or mean diffusivity (MD; Hedges' g = 0.20, 95% CI [-0.01, 0.41]). Subgroup analyses based on specific ROIs, primary substance use, poly-substance use, and imaging technology were also explored.
Conclusion: Results of the present study suggest a consistent effect of compromised WM integrity for individuals with stimulant use disorders. Furthermore, no significant differences were found between cocaine and methamphetamine-based groups.
Keywords: Cocaine; Diffusion tensor imaging; Meta-analysis; Methamphetamine; Stimulant use disorder; White matter integrity.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
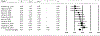
References
-
- Abhinav K, Yeh FC, Pathak S, Suski V, Lacomis D, Friedlander RM, Fernandez-Miranda JC, 2014. Advanced diffusion MRI fiber tracking in neurosurgical and neurodegenerative disorders and neuroanatomical studies: A review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis 1842, 2286–2297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

