Outcomes of natalizumab treatment within 3 years of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis diagnosis: a prespecified 2-year interim analysis of STRIVE
- PMID: 31176355
- PMCID: PMC6555913
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-019-1337-z
Outcomes of natalizumab treatment within 3 years of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis diagnosis: a prespecified 2-year interim analysis of STRIVE
Abstract
Background: STRIVE is a multicenter, observational, open-label, single-arm study of natalizumab in anti-JC virus (JCV) seronegative patients with early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). The objective of this prespecified 2-year interim analysis was to determine the effectiveness of natalizumab in establishing and maintaining no evidence of disease activity (NEDA) in early RRMS.
Methods: Patients aged 18-65 years had an RRMS diagnosis < 3 years prior to screening, an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score ≤ 4.0, and anti-JCV antibody negative status. Magnetic resonance imaging was performed at baseline and yearly thereafter. Cumulative probabilities of 24-week-confirmed EDSS worsening and improvement were evaluated at 2 years. NEDA (no 24-week-confirmed EDSS worsening, no relapses, no gadolinium-enhancing lesions, and no new/newly enlarging T2-hyperintense lesions) was evaluated over 2 years. The Symbol Digit Modalities Test (SDMT) and Multiple Sclerosis Impact Score (MSIS-29) were assessed at baseline and 1 and 2 years. Statistical analysis used summary statistics and frequency distributions.
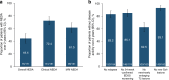
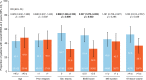
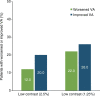
Results: The study population (N = 222) had early RRMS, with mean (standard deviation [SD]) time since diagnosis of 1.6 (0.77) years and mean (SD) baseline EDSS score of 2.0 (1.13). NEDA was achieved in 105 of 187 patients (56.1%) during year 1 and 120 of 163 (73.6%) during year 2. Over 2 years, 76 of 171 patients (44.4%) attained overall NEDA. Probabilities of 24-week-confirmed EDSS worsening and improvement were 14.1% and 28.4%, respectively. After 2 years, patients exhibited significant improvements from baseline in SDMT (n = 158; mean [SD]: 4.3 [11.8]; p < 0.001) and MSIS-29 physical (n = 153; mean [SD]: - 3.9 [14.7]; p = 0.001), psychological (n = 152; mean [SD]: - 2.0 [7.9]; p < 0.001), and quality-of-life (n = 153; mean [SD]: - 6.0 [21.3]; p < 0.001) scores.
Conclusions: These results support natalizumab's effectiveness over 2 years, during which nearly half of early RRMS patients achieved NEDA. During year 2, nearly 75% of patients exhibited NEDA. Over 2 years, patients continued to experience significant cognitive and quality-of-life benefits. These results are limited by the lack of a comparator group to determine the extent of a placebo effect.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov, NCT01485003 , registered 5 December 2011.
Keywords: Anti-JCV antibody; Brain atrophy; Natalizumab; No evidence of disease activity; Optical coherence tomography; Patient-reported outcomes; Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
JP has received fees from Acorda, Biogen, Genzyme, and Teva. RJF has received consulting fees from Actelion, Biogen, Genentech, Mallinckrodt, MedDay, Novartis, Teva, and XenoPort, advisory board fees from Biogen and Novartis, and grant/research support from Novartis. RB has received consulting fees from Biogen, Sanofi, and Teva and grant/research support from Biogen. LB has received consulting fees from Biogen and Genzyme. SG has received consulting fees from Biogen. SM, CH, and LL are employees of and hold stock and/or stock options in Biogen. SS is an employee of Cytel.
Figures



References
-
- Havrdova E, Galetta S, Hutchinson M, Stefoski D, Bates D, Polman CH, et al. Effect of natalizumab on clinical and radiological disease activity in multiple sclerosis: a retrospective analysis of the Natalizumab safety and efficacy in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (AFFIRM) study. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:254–260. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70021-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

