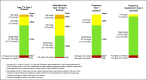
Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range
- PMID: 31177185
- PMCID: PMC6973648
- DOI: 10.2337/dci19-0028
Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range
Abstract
Improvements in sensor accuracy, greater convenience and ease of use, and expanding reimbursement have led to growing adoption of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). However, successful utilization of CGM technology in routine clinical practice remains relatively low. This may be due in part to the lack of clear and agreed-upon glycemic targets that both diabetes teams and people with diabetes can work toward. Although unified recommendations for use of key CGM metrics have been established in three separate peer-reviewed articles, formal adoption by diabetes professional organizations and guidance in the practical application of these metrics in clinical practice have been lacking. In February 2019, the Advanced Technologies & Treatments for Diabetes (ATTD) Congress convened an international panel of physicians, researchers, and individuals with diabetes who are expert in CGM technologies to address this issue. This article summarizes the ATTD consensus recommendations for relevant aspects of CGM data utilization and reporting among the various diabetes populations.
© 2019 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Lind M, Polonsky W, Hirsch IB, et al. . Continuous glucose monitoring vs conventional therapy for glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes treated with multiple daily insulin injections: the GOLD randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017;317:379–387 - PubMed
-
- Beck RW, Riddlesworth T, Ruedy K, et al. .; DIAMOND Study Group . Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: The DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017;317:371–378 - PubMed
-
- Beck RW, Riddlesworth TD, Ruedy K, et al. .; DIAMOND Study Group . Continuous glucose monitoring versus usual care in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving multiple daily insulin injections: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2017;167:365–374 - PubMed
-
- Polonsky WH, Hessler D, Ruedy KJ, Beck RW; DIAMOND Study Group . The impact of continuous glucose monitoring on markers of quality of life in adults with type 1 diabetes: further findings from the DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care 2017;40:736–741 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical