Diagnostic Accuracy of Advanced Imaging in Cardiac Sarcoidosis
- PMID: 31177817
- PMCID: PMC6653689
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.118.008975
Diagnostic Accuracy of Advanced Imaging in Cardiac Sarcoidosis
Abstract
Background The diagnostic yield of cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) by endomyocardial biopsy is limited. Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may facilitate noninvasive diagnosis, but the accuracy of this approach is not well defined. We aimed to correlate findings from FDG PET and cardiac MRI with histological findings from explanted hearts of patients who underwent cardiac transplantation. Methods We analyzed the explanted heart histology for all patients who underwent cardiac transplant at our center from April 2008 to July 2018 and had pretransplant FDG PET (n=18) or cardiac MRI (n=31). The likelihood of CS based on FDG PET or cardiac MRI was categorized in a blinded fashion using a previously published method. RESULTS: Using a CS probable cutoff for FDG PET resulted in a sensitivity of 100.0% (95% CI, 54.1%-100.0%) and a specificity of 33.3% (95% CI, 9.9%-65.1%). Three of the 9 CS probable by FDG PET cases were found to be arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. The test characteristics of cardiac MRI are more challenging to comment on using our data as there was only one confirmed case of CS on post-transplant histological assessment. Of the 8 CS highly probable or probable cases by cardiac MRI, 3 were found to be dilated cardiomyopathy, and 2 were found to be end-stage hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Conclusions FDG PET and cardiac MRI can help facilitate the diagnosis of CS in patients with advanced heart failure with a high degree of sensitivity but lower specificity.
Keywords: biopsy; cardiomyopathy; heart failure; sarcoidosis; transplantation.
Figures
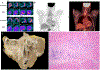


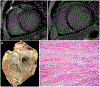
Comment in
-
Advanced Cardiac Imaging and the Complexity of Diagnosing Cardiac Sarcoidosis.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Jun;12(6):e009275. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009275. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31177819 No abstract available.
-
Response by Divakaran et al to Letter Regarding Article, "Diagnostic Accuracy of Advanced Imaging in Cardiac Sarcoidosis: An Imaging-Histologic Correlation Study in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Transplantation".Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Aug;12(8):e009622. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009622. Epub 2019 Aug 15. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31412718 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Letter by Birnie et al Regarding Article, "Diagnostic Accuracy of Advanced Imaging in Cardiac Sarcoidosis: Implications for the Diagnosis of Isolated Cardiac Sarcoidosis".Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Aug;12(8):e009614. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009614. Epub 2019 Aug 15. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31412720 No abstract available.
References
-
- Iannuzzi MC, Fontana JR. Sarcoidosis: clinical presentation, immunopathogenesis, and therapeutics. JAMA. 2011;305:391–399. - PubMed
-
- Birnie DH, Nery PB, Ha AC, Beanlands RS. Cardiac Sarcoidosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:411–421. - PubMed
-
- McGrath DS, Goh N, Foley PJ, du Bois RM. Sarcoidosis: genes and microbes--soil or seed? Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2001;18:149–164. - PubMed
-
- Silverman KJ, Hutchins GM, Bulkley BH. Cardiac sarcoid: a clinicopathologic study of 84 unselected patients with systemic sarcoidosis. Circulation. 1978;58:1204–1211. - PubMed
-
- Iwai K, Tachibana T, Takemura T, Matsui Y, Kitaichi M, Kawabata Y. Pathological studies on sarcoidosis autopsy. I. Epidemiological features of 320 cases in Japan. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1993;43:372–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

