Differentially expressed genes between systemic sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 31178673
- PMCID: PMC6549285
- DOI: 10.1186/s41065-019-0091-y
Differentially expressed genes between systemic sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Evidence is accumulating to characterise the key differences between systemic sclerosis (SSc) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which are similar but distinct systemic autoimmune diseases. However, the differences at the genetic level are not yet clear. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to identify key differential genes between patients with SSc and RA.
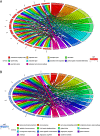
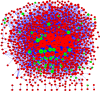
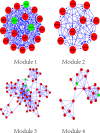
Methods: The Gene Expression Omnibus database was used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between SSc and RA biopsies. The DEGs were then functionally annotated using Gene Ontology (GO) terms and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways with the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) tools. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed with Cytoscape software. The Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE) plugin was also used to evaluate the biological importance of the constructed gene modules.
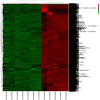
Results: A total of 13,556 DEGs were identified between the five SSc patients and seven RA patients, including 13,465 up-regulated genes and 91 down-regulated genes. Interestingly, the most significantly enriched GO terms of up- and down-regulated genes were related to extracellular involvement and immune activity, respectively, and the top six highly enriched KEGG pathways were related to the same processes. In the PPI network, the top 10 hub nodes and top four modules harboured the most relevant genes contributing to the differences between SSc and RA, including key genes such as IL6, EGF, JUN, FGF2, BMP2, FOS, BMP4, LRRK2, CTNNB1, EP300, CD79, and CXCL13.
Conclusions: These genes such as IL6, EGF, JUN, FGF2, BMP2, FOS, BMP4, LRRK2, CTNNB1, EP300, CD79, and CXCL13 can serve as new targets for focused research on the distinct molecular pathogenesis of SSc and RA. Furthermore, these genes could serve as potential biomarkers for differential diagnoses or therapeutic targets for treatment.
Keywords: Differentially expressed genes; Gene expression data; Key genes; Microarray; Rheumatoid arthritis; Systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Mar 27;25:2246-2256. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915451. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 30916045 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration and Identification of Potential Biomarkers and Immune Cell Infiltration Analysis in Synovial Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2025 Feb;28(2):e70137. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.70137. Int J Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 39953769
-
Identification of differential key biomarkers in the synovial tissue between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analysis.Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Dec;40(12):5103-5110. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05825-1. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34224029
-
Gene expression profiling meta-analysis reveals novel gene signatures and pathways shared between tuberculosis and rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 7;14(3):e0213470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213470. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30845171 Free PMC article.
-
Skin Gene Expression Profiles in Systemic Sclerosis: From Clinical Stratification to Precision Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 8;24(16):12548. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612548. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive analysis by integrating gene expression, protein-protein interactions and gene ontology data.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 8;14(11):e0224632. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224632. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31703070 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of ALDH6A1 is a New Marker of Muscle Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Feb 25;15:2137-2147. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S343727. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35241929 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Main Active Components and Mechanism of Wang Bi Tablet in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Integrative Pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 4;12:669551. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.669551. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34149422 Free PMC article.
-
MYLK*FLNB and DOCK1*LAMA2 gene-gene interactions associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the focal adhesion pathway.Front Genet. 2024 May 13;15:1375036. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1375036. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38803542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chitale S, Ciapetti A, Hodgson R, Grainger A, O'Connor P, Goodson NJ, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and musculoskeletal ultrasonography detect and characterize covert inflammatory arthropathy in systemic sclerosis patients with arthralgia. Rheumatology. 2010;49(12):2357–2361. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq268. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wasserman A. Rheumatoid arthritis: common questions about diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2018;97(7):455–462. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

