Effective Delivery of Hypertrophic miRNA Inhibitor by Cholesterol-Containing Nanocarriers for Preventing Pressure Overload Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy
- PMID: 31179215
- PMCID: PMC6548964
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201900023
Effective Delivery of Hypertrophic miRNA Inhibitor by Cholesterol-Containing Nanocarriers for Preventing Pressure Overload Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy
Abstract
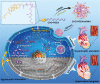
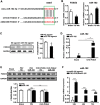
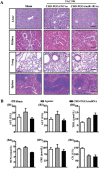
Persistent cardiac hypertrophy causes heart failure and sudden death. Gene therapy is a promising intervention for this disease, but is limited by the lack of effective delivery systems. Herein, it is reported that CHO-PGEA (cholesterol (CHO)-terminated ethanolamine-aminated poly(glycidyl methacrylate)) can efficiently condense small RNAs into nanosystems for preventing cardiac hypertrophy. CHO-PGEA contains two features: 1) lipophilic cholesterol groups enhance transfection efficiency in cardiomyocytes, 2) abundant hydrophilic hydroxyl groups benefit biocompatibility. miR-182, which is known to downregulate forkhead box O3, is selected as an intervention target and can be blocked by synthetic small RNA inhibitor of miR-182 (miR-182-in). CHO-PGEA can efficiently deliver miR-182-in into hearts. In the mice with aortic coarctation, CHO-PEGA/miR-182-in significantly suppresses cardiac hypertrophy without organ injury. This work demonstrates that CHO-PGEA/miRNA nanosystems are very promising for RNA-based therapeutics to treat heart diseases.
Keywords: cardiac hypertrophy; cardiomyocyte transfection; gene therapy; miRNA delivery; nanocarriers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CRISPR/Cas9 Delivery Mediated with Hydroxyl-Rich Nanosystems for Gene Editing in Aorta.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019 Apr 20;6(12):1900386. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900386. eCollection 2019 Jun 19. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 31380173 Free PMC article.
-
Rodlike Supramolecular Nanoassemblies of Degradable Poly(Aspartic Acid) Derivatives and Hydroxyl-Rich Polycations for Effective Delivery of Versatile Tumor-Suppressive ncRNAs.Small. 2018 Mar;14(9). doi: 10.1002/smll.201703152. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Small. 2018. PMID: 29280338
-
miR-206 Mediates YAP-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and Survival.Circ Res. 2015 Oct 23;117(10):891-904. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306624. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 26333362 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of polycation with hydroxyls for enhanced delivery of miRNA in osteosarcoma therapy.Biomater Sci. 2022 May 31;10(11):2844-2856. doi: 10.1039/d2bm00253a. Biomater Sci. 2022. PMID: 35445231
-
Multi-arm carriers composed of an antioxidant lignin core and poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-poly(ethylene glycol)methacrylate) derivative arms for highly efficient gene delivery.J Mater Chem B. 2015 Sep 14;3(34):6897-6904. doi: 10.1039/c5tb01202c. Epub 2015 Aug 6. J Mater Chem B. 2015. PMID: 32262538
Cited by
-
Biomedical polymers: synthesis, properties, and applications.Sci China Chem. 2022;65(6):1010-1075. doi: 10.1007/s11426-022-1243-5. Epub 2022 Apr 24. Sci China Chem. 2022. PMID: 35505924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-133b-3p attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy through the inhibition of apoptosis by targeting CDIP1.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025 Feb 12;57(6):916-926. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024181. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025. PMID: 39943804 Free PMC article.
-
m6A RNA Methylation in Cardiovascular Diseases.Mol Ther. 2020 Oct 7;28(10):2111-2119. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.08.010. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32910911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-27b-3p down-regulates FGF1 and aggravates pathological cardiac remodelling.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Jul 20;118(9):2139-2151. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab248. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 34358309 Free PMC article.
-
RNA methylation in vascular disease: a systematic review.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022 Dec 19;17(1):323. doi: 10.1186/s13019-022-02077-1. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022. PMID: 36536469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oka T., Akazawa H., Naito A. T., Komuro I., Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 565. - PubMed
-
- Hu M., Zhang Z., Liu B., Zhang S., Chai R., Chen X., Kong T., Zhang F., Zhang J., Liu S., Liu N., Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 2421. - PubMed
-
- Ucar A., Gupta S. K., Fiedler J., Erikci E., Kardasinski M., Batkai S., Dangwal S., Kumarswamy R., Bang C., Holzmann A., Remke J., Caprio M., Jentzsch C., Engelhardt S., Geisendorf S., Glas C., Hofmann T. G., Nessling M., Richter K., Schiffer M., Carrier L., Napp L. C., Bauersachs J., Chowdhury K., Thum T., Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1078. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brunet A., Bonni A., Zigmond M. J., Lin M. Z., Juo P., Hu L. S., Anderson M. J., Arden K. C., Blenis J., Greenberg M. E., Cell 1999, 96, 857. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
