A Dose Escalation Study of Trientine Plus Carboplatin and Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin in Women With a First Relapse of Epithelial Ovarian, Tubal, and Peritoneal Cancer Within 12 Months After Platinum-Based Chemotherapy
- PMID: 31179244
- PMCID: PMC6544081
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00437
A Dose Escalation Study of Trientine Plus Carboplatin and Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin in Women With a First Relapse of Epithelial Ovarian, Tubal, and Peritoneal Cancer Within 12 Months After Platinum-Based Chemotherapy
Abstract
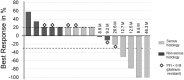
Background: Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is the leading cause of gynecological cancer-related deaths worldwide. Preclinical studies found that copper-lowering agents could re-sensitize platinum-resistant cancer cells by enhancing the human copper transporter 1 (hCtr1)-mediated uptake of platinum. In the clinic, re-sensitization of platinum-resistance in relapsed EOC has been discovered by the application of trientine plus platinum (NCT01178112). However, no pharmacokinetic data of trientine has been reported in cancer patients. Purpose: Our study aimed to explore the safety and activity of trientine combined with carboplatin and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) in patients with EOC, tubal, and peritoneal cancer who experienced disease progression during platinum-based chemotherapy or showed relapse <12 months after completing first-line chemotherapy. Also, we aimed to demonstrate pharmacokinetic parameters and to discover potential biomarkers in our EOC patients. Methods: In this dose escalation study, 18 Asian patients in six dosing cohorts received fixed doses of carboplatin (AUC 4) and PLD (LipoDox®, TTY Biopharm Co. Ltd., Taipei, Taiwan) (40 mg/m2, day 1 per 4-week cycle), and escalated daily trientine doses (range: 300-1800 mg; initiated 7 days before the 1st combination cycle) according to a 3 + 3 design. Results: No dose-limiting toxicity or treatment-related death was observed. Four patients (22.2%) developed grade 3 drug-related adverse events (AEs), whereas no grade 4 AEs were encountered. Anemia and grade 2 dizziness were the most common hematological toxicity and neurotoxicity, respectively. In a pharmacokinetics comparison with healthy volunteers in the literature, our patients achieved greater absorption after oral trientinem, and more rapid elimination of triethylenetetramine dihydrochloride at high doses. The clinical benefit rate was 33.3 and 50.0% in the platinum-resistant and the partially platinum-sensitive group, respectively. A high baseline serum iron level and low serum copper level might help differentiate subgroups of patients with different clinical responses. Nevertheless, no associations of the clinical response with the levels of serum hCtr1, ceruloplasmin, or copper were observed. Conclusion: Combination therapy with carboplatin, trientine, and PLD was well-tolerated and safe. Our results encourage the development of a future phase II trial. Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov # NCT03480750.
Keywords: adverse effect; carboplatin; ceruloplasmin; copper; human copper transporter 1; ovarian cancer; pegylated liposomal doxorubicin; trientine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploratory study of carboplatin plus the copper-lowering agent trientine in patients with advanced malignancies.Invest New Drugs. 2014 Jun;32(3):465-72. doi: 10.1007/s10637-013-0051-8. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Invest New Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24306314 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1b safety study of farletuzumab, carboplatin and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in patients with platinum-sensitive epithelial ovarian cancer.Gynecol Oncol. 2016 Feb;140(2):210-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.11.031. Epub 2015 Nov 28. Gynecol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26644263 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Overcoming platinum resistance through the use of a copper-lowering agent.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Jun;11(6):1221-5. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0864. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22491798 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in ovarian cancer treatment].Ginekol Pol. 2009 Aug;80(8):615-9. Ginekol Pol. 2009. PMID: 19824461 Review. Polish.
-
Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin combined with carboplatin: a rational treatment choice for advanced ovarian cancer.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2010 Jan;73(1):23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2009.08.004. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2010. PMID: 19782576 Review.
Cited by
-
Copper Dyshomeostasis and Diabetic Complications: Chelation Strategies for Management.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025;25(4):277-292. doi: 10.2174/0113895575308206240911104945. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39328144 Review.
-
Real-World Study of Adding Bevacizumab to Chemotherapy for Ovarian, Tubal, and Peritoneal Cancer as Front-Line or Relapse Therapy (ROBOT): 8-Year Experience.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 14;10:1095. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01095. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32760668 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting regulated cell death pathways in cancers for effective treatment: a comprehensive review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Nov 15;12:1462339. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1462339. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39620145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cuproptosis-related genes and agents: implications in tumor drug resistance and future perspectives.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 8;16:1559236. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1559236. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40406488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing an analytical method for quantification of trientine based on modified silver nanoparticles.BMC Chem. 2023 Nov 8;17(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13065-023-01068-0. BMC Chem. 2023. PMID: 37941066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Bishop K, Kosary CL, et al. (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2014. Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA. editors. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; Available online at: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2014/, based on November 2016 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2017 (accessed August 11, 2018).
Publication types
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

