An Anti-CD3 Antibody, Teplizumab, in Relatives at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 31180194
- PMCID: PMC6776880
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1902226
An Anti-CD3 Antibody, Teplizumab, in Relatives at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes
Erratum in
-
An Anti-CD3 Antibody, Teplizumab, in Relatives at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 6;382(6):586. doi: 10.1056/NEJMx190033. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32023396 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease that leads to destruction of insulin-producing beta cells and dependence on exogenous insulin for survival. Some interventions have delayed the loss of insulin production in patients with type 1 diabetes, but interventions that might affect clinical progression before diagnosis are needed.
Methods: We conducted a phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of teplizumab (an Fc receptor-nonbinding anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody) involving relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes who did not have diabetes but were at high risk for development of clinical disease. Patients were randomly assigned to a single 14-day course of teplizumab or placebo, and follow-up for progression to clinical type 1 diabetes was performed with the use of oral glucose-tolerance tests at 6-month intervals.
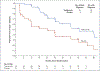
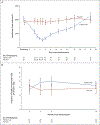
Results: A total of 76 participants (55 [72%] of whom were ≤18 years of age) underwent randomization - 44 to the teplizumab group and 32 to the placebo group. The median time to the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes was 48.4 months in the teplizumab group and 24.4 months in the placebo group; the disease was diagnosed in 19 (43%) of the participants who received teplizumab and in 23 (72%) of those who received placebo. The hazard ratio for the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes (teplizumab vs. placebo) was 0.41 (95% confidence interval, 0.22 to 0.78; P = 0.006 by adjusted Cox proportional-hazards model). The annualized rates of diagnosis of diabetes were 14.9% per year in the teplizumab group and 35.9% per year in the placebo group. There were expected adverse events of rash and transient lymphopenia. KLRG1+TIGIT+CD8+ T cells were more common in the teplizumab group than in the placebo group. Among the participants who were HLA-DR3-negative, HLA-DR4-positive, or anti-zinc transporter 8 antibody-negative, fewer participants in the teplizumab group than in the placebo group had diabetes diagnosed.
Conclusions: Teplizumab delayed progression to clinical type 1 diabetes in high-risk participants. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01030861.).
Copyright © 2019 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
Traveling down the Long Road to Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Prevention.N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 15;381(7):666-667. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1907458. Epub 2019 Jun 9. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31180193 No abstract available.
-
Teplizumab delays onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019 Aug;15(8):437. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0233-3. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31243389 No abstract available.
-
Teplizumab in Relatives at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 7;381(19):1879. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1912500. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31693815 No abstract available.
-
Teplizumab in Relatives at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 7;381(19):1879. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1912500. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31693816 No abstract available.
-
Teplizumab in Relatives at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 7;381(19):1879-1880. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1912500. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31693817 No abstract available.
-
Modulating the immune system to delay the clinical onset of type 1 diabetes.Kidney Int. 2020 Feb;97(2):248-250. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.10.010. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 31980070 No abstract available.
References
-
- Miller KM, Foster NC, Beck RW, et al. Current state of type 1 diabetes treatment in the U.S.: updated data from the T1D Exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Care 2015;38:971–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DP3 DK101122/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103282/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000445/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000114/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000645/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001857/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002537/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001872/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002529/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI09565/US/United States/United States
- U01 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002535/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057846/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000114/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103266/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI009565/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000064/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR002366/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR001872/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000142/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068678/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106994/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR002529/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR001082/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002366/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR002537/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK097835/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR001857/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103180/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085504/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
