Mechanical loading stimulates hypertrophy in tissue-engineered skeletal muscle: Molecular and phenotypic responses
- PMID: 31180593
- PMCID: PMC6771594
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28923
Mechanical loading stimulates hypertrophy in tissue-engineered skeletal muscle: Molecular and phenotypic responses
Abstract
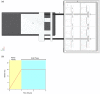
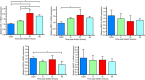
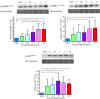
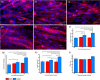
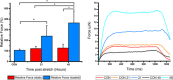
Mechanical loading of skeletal muscle results in molecular and phenotypic adaptations typified by enhanced muscle size. Studies on humans are limited by the need for repeated sampling, and studies on animals have methodological and ethical limitations. In this investigation, three-dimensional skeletal muscle was tissue-engineered utilizing the murine cell line C2C12, which bears resemblance to native tissue and benefits from the advantages of conventional in vitro experiments. The work aimed to determine if mechanical loading induced an anabolic hypertrophic response, akin to that described in vivo after mechanical loading in the form of resistance exercise. Specifically, we temporally investigated candidate gene expression and Akt-mechanistic target of rapamycin 1 signalling along with myotube growth and tissue function. Mechanical loading (construct length increase of 15%) significantly increased insulin-like growth factor-1 and MMP-2 messenger RNA expression 21 hr after overload, and the levels of the atrophic gene MAFbx were significantly downregulated 45 hr after mechanical overload. In addition, p70S6 kinase and 4EBP-1 phosphorylation were upregulated immediately after mechanical overload. Maximal contractile force was augmented 45 hr after load with a 265% increase in force, alongside significant hypertrophy of the myotubes within the engineered muscle. Overall, mechanical loading of tissue-engineered skeletal muscle induced hypertrophy and improved force production.
Keywords: hypertrophy; mTORC1; myotubes; skeletal muscle; tissue engineering.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Physiology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Adams, G. R. , Hather, B. M. , Baldwin, K. M. , & Dudley, G. A. (1993). Skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain composition and resistance training. Journal of Applied Physiology, 74(2), 911–915. http://hdl.handle.net/2060/19970022797 - PubMed
-
- Bamman, M. M. , Shipp, J. R. , Jiang, J. , Gower, B. A. , Hunter, G. R. , Goodman, A. , & Urban, R. J. (2001). Mechanical load increases muscle IGF‐I and androgen receptor mRNA concentrations in humans. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism, 280(3), E383–E390. https://doi.org/papers3://publication/uuid/1FE63A32‐B42C‐4A25‐98C6‐CF796... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

