Long-term effects of maternal choline supplementation on CA1 pyramidal neuron gene expression in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 31180719
- PMCID: PMC6704451
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201802669RR
Long-term effects of maternal choline supplementation on CA1 pyramidal neuron gene expression in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
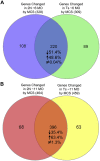
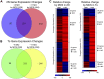
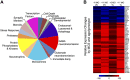
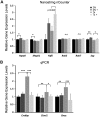
Choline is critical for normative function of 3 major pathways in the brain, including acetylcholine biosynthesis, being a key mediator of epigenetic regulation, and serving as the primary substrate for the phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase pathway. Sufficient intake of dietary choline is critical for proper brain function and neurodevelopment. This is especially important for brain development during the perinatal period. Current dietary recommendations for choline intake were undertaken without critical evaluation of maternal choline levels. As such, recommended levels may be insufficient for both mother and fetus. Herein, we examined the impact of perinatal maternal choline supplementation (MCS) in a mouse model of Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease, the Ts65Dn mouse relative to normal disomic littermates, to examine the effects on gene expression within adult offspring at ∼6 and 11 mo of age. We found MCS produces significant changes in offspring gene expression levels that supersede age-related and genotypic gene expression changes. Alterations due to MCS impact every gene ontology category queried, including GABAergic neurotransmission, the endosomal-lysosomal pathway and autophagy, and neurotrophins, highlighting the importance of proper choline intake during the perinatal period, especially when the fetus is known to have a neurodevelopmental disorder such as trisomy.-Alldred, M. J., Chao, H. M., Lee, S. H., Beilin, J., Powers, B. E., Petkova, E., Strupp, B. J., Ginsberg, S. D. Long-term effects of maternal choline supplementation on CA1 pyramidal neuron gene expression in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: early choline delivery; hippocampus; laser capture microdissection; microarray; trisomic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors thank Arthur Saltzman at the Nathan Kline Institute for expert technical assistance. This study was supported by U.S. National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging Grants AG014449, AG043375, AG055328, and AG107617 and the Alzheimer’s Association. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Meck W. H., Smith R. A., Williams C. L. (1989) Organizational changes in cholinergic activity and enhanced visuospatial memory as a function of choline administered prenatally or postnatally or both. Behav. Neurosci. 103, 1234–1241 - PubMed
-
- Kelley C. M., Ash J. A., Powers B. E., Velazquez R., Alldred M. J., Ikonomovic M. D., Ginsberg S. D., Strupp B. J., Mufson E. J. (2016) Effects of maternal choline supplementation on the septohippocampal cholinergic system in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 13, 84–96 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Strupp B. J., Powers B. E., Velazquez R., Ash J. A., Kelley C. M., Alldred M. J., Strawderman M., Caudill M. A., Mufson E. J., Ginsberg S. D. (2016) Maternal choline supplementation: a potential prenatal treatment for Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 13, 97–106 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blusztajn J. K. (1998) Choline, a vital amine. Science 281, 794–795 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

