Cortical gray-white matter blurring and declarative memory impairment in MRI-negative temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 31181427
- PMCID: PMC8162756
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.05.009
Cortical gray-white matter blurring and declarative memory impairment in MRI-negative temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
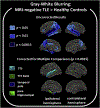
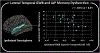
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-negative temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) may be a distinct syndrome from TLE with mesial temporal sclerosis (TLE-MTS). Imaging and neuropsychological features of TLE-MTS are well-known; yet, these features are only beginning to be described in MRI-negative TLE. This study examined whether a quantitative measure of cortical gray and white matter blurring (GWB) was elevated in the temporal lobes ipsilateral to the seizure onset zone of individuals with MRI-negative TLE relative to TLE-MTS and healthy controls (HCs) and whether GWB elevations were associated with neuropsychological comorbidity. Gray-white matter blurring from 34 cortical regions and hippocampal volumes were quantified and compared across 28 people with MRI-negative TLE, 15 people with TLE-MTS, and 51 HCs. Declarative memory was assessed with standard neuropsychological tests and the intracarotid amobarbital procedure (IAP). In the group with MRI-negative TLE (left and right onsets combined), hippocampal volumes were within normal range but GWB was elevated, relative to HCs, across several mesial and lateral temporal lobe regions ipsilateral to the seizure onset zone. Gray-white matter blurring did not differ between the groups with TLE-MTS and HC or between the groups with TLE-MTS and MRI-negative TLE. The group with MRI-negative TLE could not be distinguished from the group with TLE-MTS on any of the standard neuropsychological tests; however, ipsilateral hippocampal volumes and IAP memory scores were lower in the group with TLE-MTS than in the group with MRI-negative TLE. The group with left MRI-negative TLE had lower general cognitive abilities and verbal fluency relative to the HC group, which adds to the characterization of neuropsychological comorbidities in left MRI-negative TLE. In addition, ipsilateral IAP memory performance was reduced relative to contralateral memory performance in MRI-negative TLE, indicating some degree of ipsilateral memory dysfunction. There was no relationship between hippocampal volume and IAP memory scores in MRI-negative TLE; however, decreased ipsilateral IAP memory scores were correlated with elevated GWB in the ipsilateral superior temporal sulcus of people with left MRI-negative TLE. In sum, GWB elevations in the ipsilateral temporal lobe of people with MRI-negative TLE suggest that GWB may serve as a marker for reduced structural integrity in regions in or near the seizure onset zone. Although mesial temporal abnormalities might be the major driver of memory dysfunction in TLE-MTS, a loss of structural integrity in lateral temporal lobe regions may contribute to IAP memory dysfunction in MRI-negative TLE.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

