An Effective Primary Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vitro Model
- PMID: 31181618
- PMCID: PMC6628367
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8060555
An Effective Primary Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vitro Model
Abstract
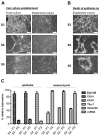
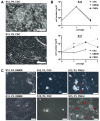
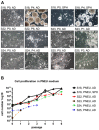
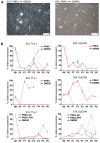
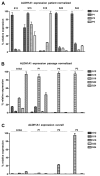
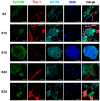
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is a highly malignant disease and research is needed to find new therapeutic approaches. Faithful experimental models are required for this purpose. Here, we describe the specific cell culture conditions enabling the efficient establishment of primary cell culture models. Whereas a classical 10% serum-containing medium resulted in the growth of fibroblast-like cells that outcompeted epithelial cells, we found that the use of specific culture conditions enabled the growth of epithelial tumor cells from HPV+ and HPV- head and neck cancer tissue applicable for research. EpCAM and high Thy-1 positivity on the cell surface were mutually exclusive and distinguished epithelial and fibroblast-like subpopulations in all primary cultures examined and thus can be used to monitor stromal contamination and epithelial cell content. Interestingly, cells of an individual patient developed tumor spheroids in suspension without the use of ultra-low attachment plates, whereas all other samples exclusively formed adherent cell layers. Spheroid cells were highly positive for ALDH1A1 and hence displayed a phenotype reminiscent of tumor stem cells. Altogether, we present a system to establish valuable primary cell culture models from head and neck cancer tissue at high efficiency that might be applicable in other tumor entities as well.
Keywords: HPV; head and neck cancer; primary cell culture; stroma; tumor spheroids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of cancer stem cell marker expression in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma shows prognostic value for aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH1A1).Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 15;867:172837. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172837. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31811857
-
Early stage mechanical remodeling of collagen surrounding head and neck squamous cell carcinoma spheroids correlates strongly with their invasion capability.Acta Biomater. 2019 Jan 15;84:280-292. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.11.046. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30500449
-
High Content Screening Characterization of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Cultures Generated in 384-Well Ultra-Low Attachment Plates to Screen for Better Cancer Drug Leads.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2019 Jan;17(1):17-36. doi: 10.1089/adt.2018.896. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2019. PMID: 30592624 Free PMC article.
-
Neck management in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: where do we stand?Med Oncol. 2019 Mar 27;36(5):40. doi: 10.1007/s12032-019-1265-1. Med Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30919135 Review.
-
Targeting Signalling Cross-Talk between Cancer Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblast through Monocarboxylate Transporters in Head and Neck Cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(11):1369-1378. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200721135230. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32698754 Review.
Cited by
-
Human papillomavirus-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells lose viability during triggered myocyte lineage differentiation.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jul 19;15(7):517. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06867-4. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39030166 Free PMC article.
-
Barcoded Orthotopic Patient-Derived Head & Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Model Demonstrating Clonal Stability and Maintenance of Cancer Driver Mutational Landscape.Cancer Med. 2025 Aug;14(15):e71137. doi: 10.1002/cam4.71137. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40792429 Free PMC article.
-
Precision Medicine in Head and Neck Cancers: Genomic and Preclinical Approaches.J Pers Med. 2022 May 24;12(6):854. doi: 10.3390/jpm12060854. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35743639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary head and neck cancer cell cultures are susceptible to proliferation of Epstein-Barr virus infected lymphocytes.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jan 13;23(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10481-y. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36639629 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Models for Combined Targeted Therapy Approaches.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 18;14(10):2484. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102484. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamangar F., Dores G.M., Anderson W.F. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: Defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:2137–2150. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.2308. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Braakhuis B.J., Snijders P.J., Keune W.J., Meijer C.J., Ruijter-Schippers H.J., Leemans C.R., Brakenhoff R.H. Genetic patterns in head and neck cancers that contain or lack transcriptionally active human papillomavirus. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004;96:998–1006. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh183. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

