BarkBase: Epigenomic Annotation of Canine Genomes
- PMID: 31181663
- PMCID: PMC6627511
- DOI: 10.3390/genes10060433
BarkBase: Epigenomic Annotation of Canine Genomes
Abstract
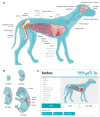
Dogs are an unparalleled natural model for investigating the genetics of health and disease, particularly for complex diseases like cancer. Comprehensive genomic annotation of regulatory elements active in healthy canine tissues is crucial both for identifying candidate causal variants and for designing functional studies needed to translate genetic associations into disease insight. Currently, canine geneticists rely primarily on annotations of the human or mouse genome that have been remapped to dog, an approach that misses dog-specific features. Here, we describe BarkBase, a canine epigenomic resource available at barkbase.org. BarkBase hosts data for 27 adult tissue types, with biological replicates, and for one sample of up to five tissues sampled at each of four carefully staged embryonic time points. RNA sequencing is complemented with whole genome sequencing and with assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq), which identifies open chromatin regions. By including replicates, we can more confidently discern tissue-specific transcripts and assess differential gene expression between tissues and timepoints. By offering data in easy-to-use file formats, through a visual browser modeled on similar genomic resources for human, BarkBase introduces a powerful new resource to support comparative studies in dogs and humans.
Keywords: ATAC-seq; RNA-seq; annotation; canine; comparative; dog; epigenomic; expression; genome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Noh H.J., Tang R., Flannick J., O’Dushlaine C., Swofford R., Howrigan D., Genereux D.P., Johnson J., van Grootheest G., Grünblatt E., et al. Integrating evolutionary and regulatory information with a multispecies approach implicates genes and pathways in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:774. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00831-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karlsson E.K., Sigurdsson S., Ivansson E., Thomas R., Elvers I., Wright J., Howald C., Tonomura N., Perloski M., Swofford R., et al. Genome-wide analyses implicate 33 loci in heritable dog osteosarcoma, including regulatory variants near CDKN2A/B. Genome Biol. 2013;14:R132. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-12-r132. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

