Design, Synthesis and Anti-Platelet Aggregation Activity Study of Ginkgolide-1,2,3-triazole Derivatives
- PMID: 31181694
- PMCID: PMC6600273
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24112156
Design, Synthesis and Anti-Platelet Aggregation Activity Study of Ginkgolide-1,2,3-triazole Derivatives
Abstract
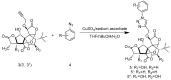
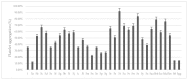
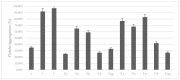
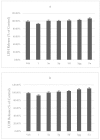
Ginkgolides are the major active component of Ginkgo biloba for inhibition of platelet activating factor receptor. An azide-alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition reaction was used to introduce a triazole nucleus into the target ginkgolide molecules. A series of ginkgolide-1,2,3-triazole conjugates with varied functional groups including benzyl, phenyl and heterocycle moieties was thus synthesized. Many of the designed derivatives showed potent antiplatelet aggregation activities with IC50 values of 5~21 nM.
Keywords: ginkgolide; inhibitor; platelet-activating factor receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Maruyama M., Terahara A., Itagaki Y., Nakanishi K. The ginkgolides. I. Isolation and characterization of the various groups. Tetrahedron Lett. 1967;8:299–302. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)71538-3. - DOI
-
- Zhang X., Li Y., Zhang L., Qin M. A new ginkgolide from Ginkgo biloba. J. China Pharm. Univ. 2009;40:306–309.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

