Salivary and Serum Interferon-Gamma/Interleukin-4 Ratio in Oral Lichen Planus Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31181785
- PMCID: PMC6630336
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina55060257
Salivary and Serum Interferon-Gamma/Interleukin-4 Ratio in Oral Lichen Planus Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
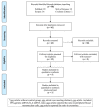
Background and Objectives: Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)/interleukin-4 (IL-4) ratio may indicate a change in the immune response with a potential pathological effect presented in oral lichen planus (OLP) patients. Herein, this meta-analysis evaluated the role of serum and salivary interferon-gamma/interleukin-4 ratio in the severity and development of OLP. Materials and Methods: The Scopus, Cochrane Library, PubMed, and Web of Science databases were systematically searched to retrieve the relevant studies published up from the database inception to March 2019. The crude mean difference (MD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated by RevMan 5.3 software using a random-effects model. A sensitivity analysis was performed on the results using the CMA 2.0 software. A total of 98 studies were retrieved from the databases, of which at last seven studies were included in this meta-analysis. Results: The findings showed that the pooled MDs of serum and salivary IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio were -0.22 (95% CI: -1.16, 0.72; p = 0.64) and 0.17 (95% CI: -1.50, 1.84; p = 0.84) in OLP patients compared to controls, respectively. In addition, the pooled MDs of serum and salivary IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio were -0.15 (95% CI: -0.53, 0.23; p = 0.43) and -0.39 (95% CI: -0.63, -0.15; p = 0.001) in patients with erythematous/ulcerative subtype compared to patients with reticular subtype, respectively. Conclusions: In conclusion, the results of meta-analysis demonstrated that serum and salivary IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio cannot play a major role in OLP development and severity.
Keywords: interferon-gamma; interleukin-4; meta-analysis; oral lichen planus; ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
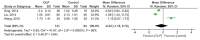
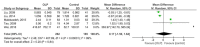
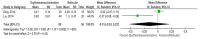
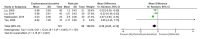
Similar articles
-
Interferon-γ and interleukin-4 detected in serum and saliva from patients with oral lichen planus.Int J Oral Sci. 2014 Mar;6(1):22-6. doi: 10.1038/ijos.2013.74. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Int J Oral Sci. 2014. PMID: 24158143 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of serum and salivary interferon-γ levels in patients with oral lichen planus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2019 Mar;127(3):210-217. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2018.11.006. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30642701
-
Serum and salivary interleukin-4 levels in patients with oral lichen planus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2019 Aug;128(2):123-131. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31097393
-
IFN-gamma and IL-4 in saliva of patients with oral lichen planus: a study in an ethnic Chinese population.Inflammation. 2009 Jun;32(3):176-81. doi: 10.1007/s10753-009-9118-2. Inflammation. 2009. PMID: 19370405
-
Serum and Salivary IgA, IgG, and IgM Levels in Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies.Medicina (Kaunas). 2018 Dec 3;54(6):99. doi: 10.3390/medicina54060099. Medicina (Kaunas). 2018. PMID: 30513983 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Salivary Biomarkers and Their Application in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of the Most Common Oral Pathologies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 21;21(14):5173. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145173. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32708341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in serum hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and erythropoietin in allergic rhinitis patients: Correlation with the Th inflammatory profile and disease comorbidities.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2023 Jan-Dec;37:3946320231196745. doi: 10.1177/03946320231196745. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37596741 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics as Potential Biological Immunomodulators in the Management of Oral Lichen Planus: What's New?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 23;23(7):3489. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073489. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel formulation of Mtb72F DNA vaccine for immunization against tuberculosis.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Jun;23(6):826-832. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.41806.9881. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32695300 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Prediction of Coronary Artery Stenosis in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease Based on Logistic Regression and Artificial Neural Network.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Mar 19;2022:3684700. doi: 10.1155/2022/3684700. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 35345521 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Lodi G., Scully C., Carrozzo M., Griffiths M., Sugerman P.B., Thongprasom K. Current controversies in oral lichen planus: Report of an international consensus meeting. Part 2. Clinical management and malignant transformation. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2005;100:164–178. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.06.076. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wei W., Sun Q., Deng Y., Wang Y., Du G., Song C., Li C., Zhu M., Chen G., Tang G. Mixed and inhomogeneous expression profile of Th1/Th2 related cytokines detected by cytometric bead array in the saliva of patients with oral lichen planus. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. 2018;126:142–151. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2018.02.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

