Obesity and the Mediterranean Diet: A Review of Evidence of the Role and Sustainability of the Mediterranean Diet
- PMID: 31181836
- PMCID: PMC6627690
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11061306
Obesity and the Mediterranean Diet: A Review of Evidence of the Role and Sustainability of the Mediterranean Diet
Abstract
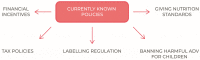
Several different socio-economic factors have caused a large portion of the population to adopt unhealthy eating habits that can undermine healthcare systems, unless current trends are inverted towards more sustainable lifestyle models. Even though a dietary plan inspired by the principles of the Mediterranean Diet is associated with numerous health benefits and has been demonstrated to exert a preventive effect towards numerous pathologies, including obesity, its use is decreasing and it is now being supplanted by different nutritional models that are often generated by cultural and social changes. Directing governments' political actions towards spreading adherence to the Mediterranean Diet's principles as much as possible among the population could help to tackle the obesity epidemic, especially in childhood. This document intends to reiterate the importance of acting in certain age groups to stop the spread of obesity and proceeds with a critical review of the regulatory instruments used so far, bearing in mind the importance of the scientific evidence that led to the consideration of the Mediterranean Diet as not just a food model, but also as the most appropriate regime for disease prevention, a sort of complete lifestyle plan for the pursuit of healthcare sustainability.
Keywords: Mediterranean Diet; childhood obesity; health communication; healthy lifestyle; public health policy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bach-Faig A., Berry E.M., Lairon D., Reguant J., Trichopoulou A., Dernini S., Medina F.X., Battino M., Belahsen R., Miranda G., et al. Mediterranean Diet Foundation Expert Group. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011;14:2274–2284. doi: 10.1017/S1368980011002515. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marventano S., Kolacz P., Castellano S., Galvano F., Buscemi S., Mistretta A., Grosso G. A review of recent evidence in human studies of n-3 and n-6 PUFA intake on cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and depressive disorders: Does the ratio really matter? Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015 doi: 10.3109/09637486.2015.1077790. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical