Preclinical Evaluation of 1,2-Diamino-4,5-Dibromobenzene in Genetically Engineered Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 31181844
- PMCID: PMC6627568
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8060563
Preclinical Evaluation of 1,2-Diamino-4,5-Dibromobenzene in Genetically Engineered Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
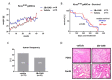
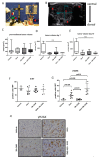
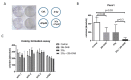
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is highly resistant to standard chemo- and radiotherapy. Recently, a new class of non-platinum-based halogenated molecules (called FMD compounds) was discovered that selectively kills cancer cells. Here, we investigate the potential of 1,2-Diamino-4,5-dibromobenzene (2Br-DAB) in combination with standard chemotherapy and radiotherapy in murine and human PDAC. Methods: Cell viability and colony formation was performed in human (Panc1, BxPC3, PaTu8988t, MiaPaCa) and three murine LSL-KrasG12D/+;LSL-Trp53R172H/+;Pdx-1-Cre (KPC) pancreatic cancer cell lines. In vivo, preclinical experiments were conducted in LSL-KrasG12D/+;p48-Cre (KC) and KPC mice using 2Br-DAB (7 mg/kg, i.p.), +/- radiation (10 × 1.8 Gy), gemcitabine (100 mg/kg, i.p.), or a combination. Tumor growth and therapeutic response were assessed by high-resolution ultrasound and immunohistochemistry. Results: 2Br-DAB significantly reduced cell viability in human and murine pancreatic cancer cell lines in a dose-dependent manner. In particular, colony formation in human Panc1 cells was significantly decreased upon 25 µM 2Br-DAB + radiation treatment compared with vehicle control (p = 0.03). In vivo, 2Br-DAB reduced tumor frequency in KC mice. In the KPC model, 2Br-DAB or gemcitabine monotherapy had comparable therapeutic effects. Furthermore, the combination of gemcitabine and 2Br-DAB or 2Br-DAB and 18 Gy irradiation showed additional antineoplastic effects. Conclusions: 2Br-DAB is effective in killing pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. 2Br-DAB was not toxic in vivo, and additional antineoplastic effects were observed in combination with irradiation.
Keywords: 1,2-Diamino-4,5-dibromobenzene; GEMMs; chemoresistance; femtomedicine compounds; pancreatic cancer; radiation therapy; radiosensitizer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of gemcitabine metabolizing enzymes and stromal components reveal complexities of preclinical pancreatic cancer models for therapeutic testing.Neoplasia. 2024 Jul;53:101002. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101002. Epub 2024 May 13. Neoplasia. 2024. PMID: 38744194 Free PMC article.
-
IL6 Receptor Blockade Enhances Chemotherapy Efficacy in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Sep;16(9):1898-1908. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0899. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28611107 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin prolongs survival and reduces the number of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in a genetically engineered mouse model of pancreatic cancer.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2013 Oct;398(7):989-96. doi: 10.1007/s00423-013-1105-2. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2013. PMID: 23989613
-
Differences between KC and KPC pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma mice models, in terms of their modeling biology and their clinical relevance.Pancreatology. 2020 Jan;20(1):79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2019.11.006. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Pancreatology. 2020. PMID: 31780287 Review.
-
GEMMs as preclinical models for testing pancreatic cancer therapies.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Oct 1;8(10):1185-200. doi: 10.1242/dmm.021055. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 26438692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innovative Experimental Ultrasound and US-Related Techniques Using the Murine Model in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 14;12(24):7677. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247677. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38137745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulated GDF-15 expression facilitates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through orphan receptor GFRAL.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Nov 17;12(22):22564-22581. doi: 10.18632/aging.103830. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33201838 Free PMC article.
-
Reaction Cycles of Halogen Species in the Immune Defense: Implications for Human Health and Diseases and the Pathology and Treatment of COVID-19.Cells. 2020 Jun 13;9(6):1461. doi: 10.3390/cells9061461. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32545714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burris H.A., III, Moore M.J., Andersen J., Grenn M.R., Rothenberg M.L., Modiano M.R., Cripps C.M., Portenoy R.K., Storniolo A.M., Tarassoff P., et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997;15:2403–2413. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.6.2403. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Neoptolemos J.P., Palmer D.H., Ghaneh P., E Psarelli E., Valle J.W., Halloran C.M., Faluyi O., O’Reilly D.A., Cunningham D., Wadsley J., et al. Comparison of adjuvant gemcitabine and capecitabine with gemcitabine monotherapy in patients with resected pancreatic cancer (ESPAC-4): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;389:1011–1024. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32409-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

