L2,1-GRMF: an improved graph regularized matrix factorization method to predict drug-target interactions
- PMID: 31182006
- PMCID: PMC6557743
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-019-2768-7
L2,1-GRMF: an improved graph regularized matrix factorization method to predict drug-target interactions
Abstract
Background: Predicting drug-target interactions is time-consuming and expensive. It is important to present the accuracy of the calculation method. There are many algorithms to predict global interactions, some of which use drug-target networks for prediction (ie, a bipartite graph of bound drug pairs and targets known to interact). Although these algorithms can predict some drug-target interactions to some extent, there is little effect for some new drugs or targets that have no known interaction.
Results: Since the datasets are usually located at or near low-dimensional nonlinear manifolds, we propose an improved GRMF (graph regularized matrix factorization) method to learn these flow patterns in combination with the previous matrix-decomposition method. In addition, we use one of the pre-processing steps previously proposed to improve the accuracy of the prediction.
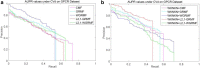
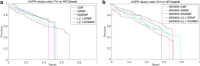
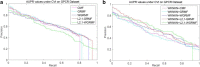
Conclusions: Cross-validation is used to evaluate our method, and simulation experiments are used to predict new interactions. In most cases, our method is superior to other methods. Finally, some examples of new drugs and new targets are predicted by performing simulation experiments. And the improved GRMF method can better predict the remaining drug-target interactions.
Keywords: Drug-target interaction prediction; Graph regularization; L2,1-norm; Manifold learning; Matrix factorization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Drug-Target Interaction Prediction with Graph Regularized Matrix Factorization.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2017 May-Jun;14(3):646-656. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2016.2530062. Epub 2016 Feb 15. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2017. PMID: 26890921
-
Graph regularized non-negative matrix factorization with prior knowledge consistency constraint for drug-target interactions prediction.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Dec 29;23(1):564. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-05119-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36581822 Free PMC article.
-
WGRCMF: A Weighted Graph Regularized Collaborative Matrix Factorization Method for Predicting Novel LncRNA-Disease Associations.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021 Jan;25(1):257-265. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.2985703. Epub 2021 Jan 5. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021. PMID: 32287024
-
Some Remarks on Prediction of Drug-Target Interaction with Network Models.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(21):2456-2468. doi: 10.2174/1568026617666170414145015. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28413948 Review.
-
Predicting Drug Synergism by Means of Non-Negative Matrix Tri-Factorization.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2022 Jul-Aug;19(4):1956-1967. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2021.3091814. Epub 2022 Aug 8. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 34166199
Cited by
-
Coupled matrix-matrix and coupled tensor-matrix completion methods for predicting drug-target interactions.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Mar 22;22(2):2161-2171. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa025. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 32186716 Free PMC article.
-
DSCMF: prediction of LncRNA-disease associations based on dual sparse collaborative matrix factorization.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 May 12;22(Suppl 3):241. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03868-w. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33980147 Free PMC article.
-
RCMF: a robust collaborative matrix factorization method to predict miRNA-disease associations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Dec 24;20(Suppl 25):686. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-3260-0. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31874608 Free PMC article.
-
DTiGEMS+: drug-target interaction prediction using graph embedding, graph mining, and similarity-based techniques.J Cheminform. 2020 Jun 29;12(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13321-020-00447-2. J Cheminform. 2020. PMID: 33431036 Free PMC article.
-
Logistic matrix factorisation and generative adversarial neural network-based method for predicting drug-target interactions.Mol Divers. 2021 Aug;25(3):1497-1516. doi: 10.1007/s11030-021-10273-9. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Mol Divers. 2021. PMID: 34297278
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

