Close Homolog of L1 Regulates Dendritic Spine Density in the Mouse Cerebral Cortex Through Semaphorin 3B
- PMID: 31182634
- PMCID: PMC6687901
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2984-18.2019
Close Homolog of L1 Regulates Dendritic Spine Density in the Mouse Cerebral Cortex Through Semaphorin 3B
Abstract
Dendritic spines in the developing mammalian neocortex are initially overproduced and then eliminated during adolescence to achieve appropriate levels of excitation in mature networks. We show here that the L1 family cell adhesion molecule Close Homolog of L1 (CHL1) and secreted repellent ligand Semaphorin 3B (Sema3B) function together to induce dendritic spine pruning in developing cortical pyramidal neurons. Loss of CHL1 in null mutant mice in both genders resulted in increased spine density and a greater proportion of immature spines on apical dendrites in the prefrontal and visual cortex. Electron microscopy showed that excitatory spine synapses with postsynaptic densities were increased in the CHL1-null cortex, and electrophysiological recording in prefrontal slices from mutant mice revealed deficiencies in excitatory synaptic transmission. Mechanistically, Sema3B protein induced elimination of spines on apical dendrites of cortical neurons cultured from wild-type but not CHL1-null embryos. Sema3B was secreted by the cortical neuron cultures, and its levels increased when cells were treated with the GABA antagonist gabazine. In vivo CHL1 was coexpressed with Sema3B in pyramidal neuron subpopulations and formed a complex with Sema3B receptor subunits Neuropilin-2 and PlexinA4. CHL1 and NrCAM, a closely related L1 adhesion molecule, localized primarily to distinct spines and promoted spine elimination to Sema3B or Sema3F, respectively. These results support a new concept in which selective spine elimination is achieved through different secreted semaphorins and L1 family adhesion molecules to sculpt functional neural circuits during postnatal maturation.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Dendritic spines in the mammalian neocortex are initially overproduced and then pruned in adolescent life through unclear mechanisms to sculpt maturing cortical circuits. Here, we show that spine and excitatory synapse density of pyramidal neurons in the developing neocortex is regulated by the L1 adhesion molecule, Close Homolog of L1 (CHL1). CHL1 mediated spine pruning in response to the secreted repellent ligand Semaphorin 3B and associated with receptor subunits Neuropilin-2 and PlexinA4. CHL1 and related L1 adhesion molecule NrCAM localized to distinct spines, and promoted spine elimination to Semaphorin 3B and -3F, respectively. These results support a new concept in which selective elimination of individual spines and nascent synapses can be achieved through the action of distinct secreted semaphorins and L1 adhesion molecules.
Keywords: Semaphorin 3B; autism spectrum disorders; cell adhesion molecule; close homolog of L1; dendritic spine; spine pruning.
Copyright © 2019 the authors.
Figures




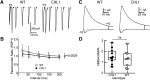
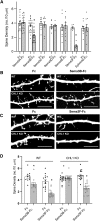
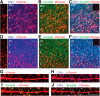

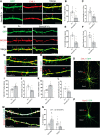
Comment in
-
A Novel Mechanism Underlying Activity-Dependent Pruning in Postnatal Prefrontal Cortex.J Neurosci. 2020 Mar 11;40(11):2186-2188. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2394-19.2020. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32161181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Neural cell adhesion molecule NrCAM regulates Semaphorin 3F-induced dendritic spine remodeling.J Neurosci. 2014 Aug 20;34(34):11274-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1774-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25143608 Free PMC article.
-
Neurocan Inhibits Semaphorin 3F Induced Dendritic Spine Remodeling Through NrCAM in Cortical Neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Oct 9;12:346. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00346. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30356641 Free PMC article.
-
Ankyrin B promotes developmental spine regulation in the mouse prefrontal cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2023 Oct 9;33(20):10634-10648. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhad311. Cereb Cortex. 2023. PMID: 37642601 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of cytoskeletal regulatory factors in the adolescent prefrontal cortex: Implications for cortical development.J Neurosci Res. 2017 May;95(5):1123-1143. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23960. Epub 2016 Oct 13. J Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 27735056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semaphorins and their receptors in lung cancer.Cancer Lett. 2009 Jan 8;273(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.05.032. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Cancer Lett. 2009. PMID: 18625544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of L1 and NCAM Adhesion Molecules in Synaptic Pruning, Plasticity, and Stabilization.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 28;9:625340. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.625340. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33585481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropilin 2/Plexin-A3 Receptors Regulate the Functional Connectivity and the Excitability in the Layers 4 and 5 of the Cerebral Cortex.J Neurosci. 2022 Jun 15;42(24):4828-4840. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1965-21.2022. Epub 2022 May 9. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35534225 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear speckle specific hnRNP D-like prevents age- and AD-related cognitive decline by modulating RNA splicing.Mol Neurodegener. 2021 Sep 22;16(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00485-w. Mol Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 34551807 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic cell adhesion molecules contribute to the pathogenesis and progression of fragile X syndrome.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jul 3;18:1393536. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1393536. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39022311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatiotemporal Control of Neuronal Remodeling by Cell Adhesion Molecules: Insights From Drosophila.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 12;16:897706. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.897706. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35645712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agresti A. (2013) Categorical data analysis, Ed 3 New York: Wiley.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
