The Functions of DNA Damage Factor RNF8 in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Cancer
- PMID: 31182912
- PMCID: PMC6535783
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.31972
The Functions of DNA Damage Factor RNF8 in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Cancer
Abstract
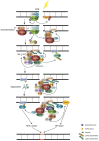
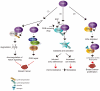
The really interesting new gene (RING) finger protein 8 (RNF8) is a central factor in DNA double strand break (DSB) signal transduction. DSB damage is the most toxic type of DNA damage to cells and is related to genomic instability. Multiple roles for RNF8 have been identified in DNA damage response as well as in other functions, such as telomere protection, cell cycle control and transcriptional regulation. These functions are closely correlated to tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Indeed, deficiency of RNF8 caused spontaneous tumorigenesis in a mouse model. Deciphering these mechanisms of RNF8 may shed light on strategies for cancer treatment. In this review, we summarize the current understanding of both classical and nonclassical functions of RNF8, and discuss its roles in the pathogenesis and progression of tumor.
Keywords: DSB; RNF8; cell cycle; telomere; transcriptional regulation; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Seki N, Hattori A, Sugano S, Suzuki Y, Nakagawara A, Ohhira M. et al. Isolation, tissue expression, and chromosomal assignment of a novel human gene which encodes a protein with RING finger motif. J Hum Genet. 1998;43:272–4. - PubMed
-
- Ito K, Adachi S, Iwakami R, Yasuda H, Muto Y, Seki N. et al. N-Terminally extended human ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s) mediate the ubiquitination of RING-finger proteins, ARA54 and RNF8. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:2725–32. - PubMed
-
- Plans V, Scheper J, Soler M, Loukili N, Okano Y, Thomson TM. The RING finger protein RNF8 recruits UBC13 for lysine 63-based self polyubiquitylation. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97:572–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

