Noninvasive Evaluation of the Pathologic Grade of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using MCF-3DCNN: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 31183380
- PMCID: PMC6512077
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9783106
Noninvasive Evaluation of the Pathologic Grade of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using MCF-3DCNN: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the diagnostic performance of deep learning with a multichannel fusion three-dimensional convolutional neural network (MCF-3DCNN) in the differentiation of the pathologic grades of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) based on dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance images (DCE-MR images).
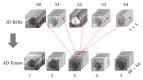
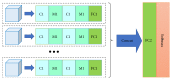
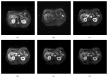
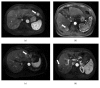
Methods and materials: Fifty-one histologically proven HCCs from 42 consecutive patients from January 2015 to September 2017 were included in this retrospective study. Pathologic examinations revealed nine well-differentiated (WD), 35 moderately differentiated (MD), and seven poorly differentiated (PD) HCCs. DCE-MR images with five phases were collected using a 3.0 Tesla MR scanner. The 4D-tensor representation was employed to organize the collected data in one temporal and three spatial dimensions by referring to the phases and 3D scanning slices of the DCE-MR images. A deep learning diagnosis model with MCF-3DCNN was proposed, and the structure of MCF-3DCNN was determined to approximate clinical diagnosis experience by taking into account the significance of the spatial and temporal information from DCE-MR images. Then, MCF-3DCNN was trained based on well-labeled samples of HCC lesions from real patient cases by experienced radiologists. The accuracy when differentiating the pathologic grades of HCC was calculated, and the performance of MCF-3DCNN in lesion diagnosis was assessed. Additionally, the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC) for distinguishing WD, MD, and PD HCCs were calculated.
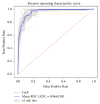
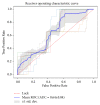
Results: MCF-3DCNN achieved an average accuracy of 0.7396±0.0104 with regard to totally differentiating the pathologic grade of HCC. MCF-3DCNN also achieved the highest diagnostic performance for discriminating WD HCCs from others, with an average AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of 0.96, 91.00%, 96.88%, and 89.62%, respectively.
Conclusions: This study indicates that MCF-3DCNN can be a promising technology for evaluating the pathologic grade of HCC based on DCE-MR images.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differentiation of well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinomas from other hepatocellular nodules in cirrhotic liver: value of SPIO-enhanced MR imaging at 3.0 Tesla.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009 Feb;29(2):328-35. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21615. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009. PMID: 19161184
-
Quantitative free-breathing dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in hepatocellular carcinoma using gadoxetic acid: correlations with Ki67 proliferation status, histological grades, and microvascular density.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018 Jun;43(6):1393-1403. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1320-3. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018. PMID: 28939963
-
Gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging predicts the histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma only in patients with Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis.Liver Transpl. 2012 Jul;18(7):850-7. doi: 10.1002/lt.23426. Liver Transpl. 2012. PMID: 22407909
-
Diagnostic performance of gadoxetic acid-enhanced liver MR imaging in the detection of HCCs and allocation of transplant recipients on the basis of the Milan criteria and UNOS guidelines: correlation with histopathologic findings.Radiology. 2015 Jan;274(1):149-60. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14140141. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Radiology. 2015. PMID: 25203131
-
Artificial intelligence in hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis: a comprehensive review of current literature.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;39(10):1994-2005. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16663. Epub 2024 Jun 23. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38923550 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the Power of AI for Enhanced Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 16;36(4):200-208. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2024.24325. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39714118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review of Current and Novel Techniques.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2024 Dec;55(4):1469-1484. doi: 10.1007/s12029-024-01094-8. Epub 2024 Aug 19. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39158837 Review.
-
Revisiting artificial intelligence diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with DIKWH framework.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 7;14:1004481. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1004481. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37007970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automatic discrimination of different sequences and phases of liver MRI using a dense feature fusion neural network: a preliminary study.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Oct;46(10):4576-4587. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03142-4. Epub 2021 May 31. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 34057565
-
State of the Art in Artificial Intelligence and Radiomics in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jun 30;11(7):1194. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11071194. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34209197 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

