A Review of the Totality of Evidence Supporting the Development of the First Adalimumab Biosimilar ABP 501
- PMID: 31183781
- PMCID: PMC6822859
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-019-00979-6
A Review of the Totality of Evidence Supporting the Development of the First Adalimumab Biosimilar ABP 501
Abstract
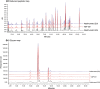
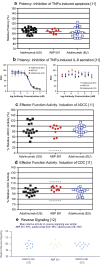
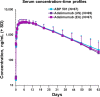
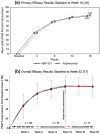
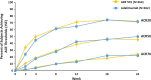
ABP 501 [United States: AMJEVITA™ (adalimumab-atto); European Union: AMGEVITA® (adalimumab)] is the first approved biosimilar to adalimumab [reference product (RP)], a monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeting tumor necrosis factor-alfa (TNF-α). ABP 501 has received approval for use in indications that adalimumab RP is approved for, except those protected by regulatory exclusivity. A systematic step-wise totality of evidence (TOE) approach formed the basis of approval of ABP 501; this involved methodical accumulation of scientifically robust comparative data supporting similarity in analytical, preclinical, and clinical [pharmacokinetics (PK)], efficacy, safety and immunogenicity) evaluations. As a foundational first step, comprehensive analytical assessments demonstrated that ABP 501 is structurally and functionally similar to adalimumab RP in critical quality attributes. Preclinical assessments confirmed similar activity in assessing mechanisms of action and toxicology. Clinical evaluation included a phase 1 PK equivalence study in healthy subjects and two comparative phase 3 studies that evaluated ABP 501 and adalimumab RP in two sensitive patient populations, plaque psoriasis (PsO) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The PK profiles of ABP 501 and adalimumab RP were similar in healthy subjects as well as patients with PsO and RA. The pivotal phase 3 study in patients with PsO demonstrated that ABP 501 was clinically similar to adalimumab RP in terms of efficacy, safety and immunogenicity in both the primary and transition phases. The pivotal phase 3 study in patients with RA also established clinical similarity between ABP 501 and adalimumab RP; an open-label extension of this study demonstrated sustained efficacy over an additional 72 weeks, with no new safety or immunogenicity concerns with ABP 501 treatment. Overall, the TOE supported the conclusion that ABP 501 is highly similar to adalimumab RP and provided scientific justification for extrapolation to all the approved indications of adalimumab RP not protected by exclusivities.Funding: Amgen Inc.
Keywords: ABP 501; Adalimumab; Ankylosing spondylitis; Biosimilar; Inflammatory bowel disease; Juvenile idiopathic arthritis; Plaque psoriasis; Psoriatic arthritis; Rheumatoid arthritis; Totality of evidence.
Figures


References
-
- Amgen Inc . AMJEVITA (adalimumab-atto) injection for subcutaneous use [prescribing information] Thousand Oaks: Amgen Inc; 2016.
-
- Amgen . AMJEVITA (adalimumab) injection for subcutaneous use [summary of product characteristics] Breda: Amgen; 2017.
-
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry: scientific considerations in demonstrating biosimilarity to a reference product. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformati.... Accessed 3 Aug 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

