GenPipes: an open-source framework for distributed and scalable genomic analyses
- PMID: 31185495
- PMCID: PMC6559338
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giz037
GenPipes: an open-source framework for distributed and scalable genomic analyses
Abstract
Background: With the decreasing cost of sequencing and the rapid developments in genomics technologies and protocols, the need for validated bioinformatics software that enables efficient large-scale data processing is growing.
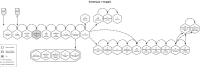
Findings: Here we present GenPipes, a flexible Python-based framework that facilitates the development and deployment of multi-step workflows optimized for high-performance computing clusters and the cloud. GenPipes already implements 12 validated and scalable pipelines for various genomics applications, including RNA sequencing, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, DNA sequencing, methylation sequencing, Hi-C, capture Hi-C, metagenomics, and Pacific Biosciences long-read assembly. The software is available under a GPLv3 open source license and is continuously updated to follow recent advances in genomics and bioinformatics. The framework has already been configured on several servers, and a Docker image is also available to facilitate additional installations.
Conclusions: GenPipes offers genomics researchers a simple method to analyze different types of data, customizable to their needs and resources, as well as the flexibility to create their own workflows.
Keywords: bioinformatics; frameworks; genomics; pipeline; workflow; workflow management systems.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


References
-
- ENCODE. The ENCODE (ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements) Project. Science. 2004;306(5696):636–40. - PubMed
-
- Stunnenberg HG, Hirst M. The International Human Epigenome Consortium: a blueprint for scientific collaboration and discovery. Cell. 2016;167(5):1145–9. - PubMed
-
- DNANexus website. https://www.dnanexus.com/. Accesed September 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

