An In Vitro Evaluation, on Polyurethane Foam Sheets, of the Insertion Torque (IT) Values, Pull-Out Torque Values, and Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) of NanoShort Dental Implants
- PMID: 31185590
- PMCID: PMC6630510
- DOI: 10.3390/polym11061020
An In Vitro Evaluation, on Polyurethane Foam Sheets, of the Insertion Torque (IT) Values, Pull-Out Torque Values, and Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) of NanoShort Dental Implants
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate, in polyurethane foam sheets, the primary implant stability of a NanoShort implant compared to a self-condenser implant and to a standard, conventional implant.
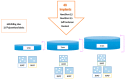
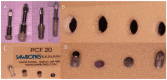
Materials and methods: Three implant designs were evaluated in the present in vitro investigation: The Test implant (NanoShort), the Control A implant (self-condenser), and the Control B implant (standard design). The study was conducted by comparing the insertion torque values, the pull-out strength values, and the resonance frequency analysis (RFA) values of the Test and Control A and B implants inserted in polyurethane foam models of different thicknesses and densities. The foam densities were 10, 20, and 30 pounds per cubic foot (pcf). Three thicknesses of polyurethane foams (1, 2, 3 mm) were evaluated for a total of 640 experimental sites.
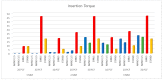
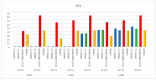
Results: The Pearson correlation showed a moderate/strong correlation between all study groups (r > 0.3) for insertion torque and pull-out strength levels. Increased stability of the Test implants was obtained in 3 mm polyurethane sheets. The 2.5 and 3.5 mm Test implants presented good stability in 3 mm polyurethane sheets of 20-30 pcf densities. The Control implants showed better results compared to the Test implants in 1, 2, and 3 mm polyurethane sheets with densities of 10, 20, and 30 pcf.
Conclusions: The NanoShort dental implant evaluated in this in vitro study showed a high level of stability in some experimental conditions, and could represent a useful tool, especially in the posterior mandible, as an alternative to vertical augmentation procedures.
Keywords: implant stability; insertion torque; polyurethane foam; pull-out strength.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Primary Stability of Dental Implants in Low-Density (10 and 20 pcf) Polyurethane Foam Blocks: Conical vs Cylindrical Implants.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 11;17(8):2617. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082617. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32290361 Free PMC article.
-
Insertion Torque, Removal Torque, and Resonance Frequency Analysis Values of Ultrashort, Short, and Standard Dental Implants: An In Vitro Study on Polyurethane Foam Sheets.J Funct Biomater. 2022 Dec 23;14(1):10. doi: 10.3390/jfb14010010. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36662057 Free PMC article.
-
An In Vitro Analysis on Polyurethane Foam Blocks of the Insertion Torque (IT) Values, Removal Torque Values (RTVs), and Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) Values in Tapered and Cylindrical Implants.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Sep 1;18(17):9238. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18179238. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34501824 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of Conical and Cylindrical Implants Inserted in an In Vitro Post-Extraction Model Using Low-Density Polyurethane Foam Blocks.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jul 18;16(14):5064. doi: 10.3390/ma16145064. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37512339 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of truncated-conical implant length on primary stability in maxillary and mandibular regions: an in vitro study using polyurethane blocks.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Dec 26;28(1):28. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05444-x. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 38147179
Cited by
-
Influence of Resonance Frequency Analysis (RFA) Measurements for Successful Osseointegration of Dental Implants During the Healing Period and Its Impact on Implant Assessed by Osstell Mentor Device.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Dec 13;7(23):4110-4115. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.716. eCollection 2019 Dec 15. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 32165961 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and Correlation of Different Devices for the Evaluation of Primary Implant Stability: An In Vitro Study.Materials (Basel). 2021 Sep 24;14(19):5537. doi: 10.3390/ma14195537. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34639933 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of a novel density measurement drill for evaluating cancellous bone density: correlation between CT value and drilling torque value in bovine ribs.Int J Implant Dent. 2025 Jan 31;11(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40729-025-00596-9. Int J Implant Dent. 2025. PMID: 39888340 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Implant Macro-Design, -Length, and -Diameter on Primary Implant Stability Depending on Different Bone Qualities Using Standard Drilling Protocols-An In Vitro Analysis.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Sep 12;14(9):469. doi: 10.3390/jfb14090469. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37754883 Free PMC article.
-
Replacement of Destructive Pull-out Test with Modal Analysis in Primary Fixation Stability Assessment of Spinal Pedicle Screw.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2022 Feb;10(2):204-212. doi: 10.22038/ABJS.2021.54294.2712. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2022. PMID: 35655738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gehrke S.A., Guirado J.L.C., Bettach R., Fabbro M.D., Martínez C.P.-A., Shibli J.A. Evaluation of the insertion torque, implant stability quotient and drilled hole quality for different drill design: An in vitro Investigation. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018;29:656–662. doi: 10.1111/clr.12808. - DOI - PubMed

