Synthesis, Characterization, and Crystal Structures of Imides Condensed with p-Phenylamino(Phenyl) Amine and Fluorescence Property
- PMID: 31185634
- PMCID: PMC6600954
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12111873
Synthesis, Characterization, and Crystal Structures of Imides Condensed with p-Phenylamino(Phenyl) Amine and Fluorescence Property
Abstract
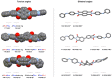
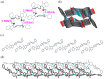
A series of aromatic diimide and monoimide compounds condensed with p-phenylamino(phenyl)amine were synthesized and confirmed by Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR), Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (13C NMR), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), Elemental Analysis (EA), and High Resolution Mass Spectroscopy (HRMS). Meanwhile, single crystal X-ray diffraction showed the existence of intermolecular N···O hydrogen bonds, which affected the thermal stabilities of corresponding compounds by the support of Thermalgravimetric Analysis (TGA) curves. The steady-state UV-vis absorption peaks of synthetic compounds 1-6 appeared in the range of 220-380 nm. Fluorescence emission spectra showed peaks in the range of 290-420 nm. Meanwhile, deep-blue or violet-blue emissions for 2, 4, and 5 in THF under excitations of 254 nm and 365 nm, respectively, were observed at room temperature in air. Furthermore, Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and cyclic voltammogram CV were conducted within -1.5-+1.5 V to show quasi-reversible behavior for conjugated compounds and irreversible behavior for less conjugated ones.
Keywords: X-ray crystal structure; electrochemistry; fluorescence; hydrogen bond; imide; p-phenylamino(phenyl)amine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Bjorgaard J.A., Köse M.E. Simulations of singlet exciton diffusion in organic semiconductors. RSC Adv. 2015;5:8432–8445. doi: 10.1039/C4RA12409J. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

