A high-density BAC physical map covering the entire MHC region of addax antelope genome
- PMID: 31185912
- PMCID: PMC6558854
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-019-5790-2
A high-density BAC physical map covering the entire MHC region of addax antelope genome
Abstract
Background: The mammalian major histocompatibility complex (MHC) harbours clusters of genes associated with the immunological defence of animals against infectious pathogens. At present, no complete MHC physical map is available for any of the wild ruminant species in the world.
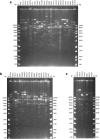
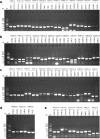
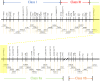
Results: The high-density physical map is composed of two contigs of 47 overlapping bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clones, with an average of 115 Kb for each BAC, covering the entire addax MHC genome. The first contig has 40 overlapping BAC clones covering an approximately 2.9 Mb region of MHC class I, class III, and class IIa, and the second contig has 7 BAC clones covering an approximately 500 Kb genomic region that harbours MHC class IIb. The relative position of each BAC corresponding to the MHC sequence was determined by comparative mapping using PCR screening of the BAC library of 192,000 clones, and the order of BACs was determined by DNA fingerprinting. The overlaps of neighboring BACs were cross-verified by both BAC-end sequencing and co-amplification of identical PCR fragments within the overlapped region, with their identities further confirmed by DNA sequencing.
Conclusions: We report here the successful construction of a high-quality physical map for the addax MHC region using BACs and comparative mapping. The addax MHC physical map we constructed showed one gap of approximately 18 Mb formed by an ancient autosomal inversion that divided the MHC class II into IIa and IIb. The autosomal inversion provides compelling evidence that the MHC organizations in all of the ruminant species are relatively conserved.
Keywords: Addax nasomaculatus; BAC; MHC; Physical map.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Organization of the Addax Major Histocompatibility Complex Provides Insights Into Ruminant Evolution.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 25;11:260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00260. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32161588 Free PMC article.
-
A physical map of a BAC clone contig covering the entire autosome insertion between ovine MHC Class IIa and IIb.BMC Genomics. 2012 Aug 16;13:398. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-398. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22897909 Free PMC article.
-
Giant panda BAC library construction and assembly of a 650-kb contig spanning major histocompatibility complex class II region.BMC Genomics. 2007 Sep 8;8:315. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-315. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17825108 Free PMC article.
-
A BAC clone-based physical map of ovine major histocompatibility complex.Genomics. 2006 Jul;88(1):88-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.02.006. Epub 2006 Apr 3. Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16595171
-
BACs as tools for the study of genomic imprinting.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:283013. doi: 10.1155/2011/283013. Epub 2010 Dec 13. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21197393 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Organization of the Addax Major Histocompatibility Complex Provides Insights Into Ruminant Evolution.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 25;11:260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00260. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32161588 Free PMC article.
-
MHC architecture in amphibians - ancestral reconstruction, gene rearrangements and duplication patterns.Genome Biol Evol. 2023 May 12;15(5):evad079. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evad079. Online ahead of print. Genome Biol Evol. 2023. PMID: 37170911 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

