MicroRNA responses associated with Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium challenge in peripheral blood: effects of miR-146a and IFN-γ in regulation of fecal bacteria shedding counts in pig
- PMID: 31186019
- PMCID: PMC6560770
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-019-1951-4
MicroRNA responses associated with Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium challenge in peripheral blood: effects of miR-146a and IFN-γ in regulation of fecal bacteria shedding counts in pig
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs are involved in a broad range of biological processes and are known to be differentially expressed in response to bacterial pathogens.
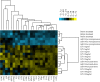
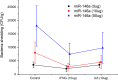
Results: The present study identified microRNA responses in porcine peripheral blood after inoculation with the human foodborne pathogen Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium strain LT2. We compared the microRNA transcriptomes of the whole blood of pigs (Duroc × Landrace × Yorkshire) at 2-days post inoculation and before Salmonella infection. The analysis identified a total of 29 differentially expressed microRNAs, most of which are implicated in Salmonella infection and immunology signaling pathways. Joint analysis of the microRNA and mRNA transcriptomes identified 24 microRNAs with binding sites that were significantly enriched in 3' UTR of differentially expressed mRNAs. Of these microRNAs, three were differentially expressed after Salmonella challenge in peripheral blood (ssc-miR-146a-5p, ssc-miR-125a, and ssc-miR-129a-5p). Expression of 23 targets of top-ranked microRNA, ssc-miR-146a-5p, was validated by real-time PCR. The effects of miR-146a, IFN-γ, and IL-6 on the regulation of fecal bacteria shedding counts in pigs were investigated by in vivo study with a Salmonella challenge model.
Conclusions: The results indicated that induction of miR-146a in peripheral blood could significantly increase the fecal bacterial load, whereas IFN-γ had the reverse effect. These microRNAs can be used to identify targets for controlling porcine salmonellosis.
Keywords: IFN-γ; Immune response; Salmonella; Swine; miR-146a; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct peripheral blood RNA responses to Salmonella in pigs differing in Salmonella shedding levels: intersection of IFNG, TLR and miRNA pathways.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028768. Epub 2011 Dec 12. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22174891 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of porcine microRNAs associated with apoptosis and NF-κB signaling pathways in response to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Gene. 2018 Nov 15;676:290-297. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.08.044. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Gene. 2018. PMID: 30099024
-
Chlortetracycline Enhances Tonsil Colonization and Fecal Shedding of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium DT104 without Major Alterations to the Porcine Tonsillar and Intestinal Microbiota.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Feb 6;85(4):e02354-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02354-18. Print 2019 Feb 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30530706 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for transcriptomic analyses of the porcine host immune response: application to Salmonella infection using microarrays.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010 Dec 15;138(4):280-91. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.10.006. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 21036404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflamm-aging microRNAs may integrate signals from food and gut microbiota by modulating common signalling pathways.Mech Ageing Dev. 2019 Sep;182:111127. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2019.111127. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Mech Ageing Dev. 2019. PMID: 31401225 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of trait-associated microRNA modules in liver transcriptome of pig fed with PUFAs-enriched supplementary diet.J Appl Genet. 2025 May;66(2):389-407. doi: 10.1007/s13353-024-00912-w. Epub 2024 Nov 15. J Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 39546271 Free PMC article.
-
Study of microRNA expression in Salmonella Typhimurium-infected porcine ileum reveals miR-194a-5p as an important regulator of the TLR4-mediated inflammatory response.Vet Res. 2022 May 21;53(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01056-7. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35598011 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA Regulatory Functions in Farm Animal Diseases, and Biomarker Potentials for Effective Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 17;22(6):3080. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063080. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium SPI-1 and SPI-2 Shape the Global Transcriptional Landscape in a Human Intestinal Organoid Model System.mBio. 2021 May 18;12(3):e00399-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00399-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34006652 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: exploring their role in farm animal disease and mycotoxin challenges.Front Vet Sci. 2024 May 13;11:1372961. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1372961. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38803799 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31402055/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2015cqr12/Yangtze Youth Talents Fund
- 2015cqn39/Yangtze Youth Fund
- Q20171305/Science and Technology Research Project of Department of Education of Hubei Province
- 2018057/College Students' Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Yangtze University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

