Regulation of the Hepatitis B virus replication and gene expression by the multi-functional protein TARDBP
- PMID: 31186504
- PMCID: PMC6560085
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-44934-5
Regulation of the Hepatitis B virus replication and gene expression by the multi-functional protein TARDBP
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Regulation of the Hepatitis B virus replication and gene expression by the multi-functional protein TARDBP.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 5;10(1):2233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58888-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32024922 Free PMC article.
Abstract
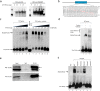
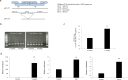
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infects the liver and is a key risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. Identification of host factors that support viral replication is important to understand mechanisms of viral replication and to develop new therapeutic strategies. We identified TARDBP as a host factor that regulates HBV. Silencing or knocking out the protein in HBV infected cells severely impaired the production of viral replicative intermediates, mRNAs, proteins, and virions, whereas ectopic expression of TARDBP rescued production of these products. Mechanistically, we found that the protein binds to the HBV core promoter, as shown by chromatin precipitation as well as mutagenesis and protein-DNA interaction assays. Using LC-MS/MS analysis, we also found that TARDBP binds to a number of other proteins known to support the HBV life cycle, including NPM1, PARP1, Hsp90, HNRNPC, SFPQ, PTBP1, HNRNPK, and PUF60. Interestingly, given its key role as a regulator of RNA splicing, we found that TARDBP has an inhibitory role on pregenomic RNA splicing, which might help the virus to export its non-canonical RNAs from the nucleus without being subjected to unwanted splicing, even though mRNA nuclear export is normally closely tied to RNA splicing. Taken together, our results demonstrate that TARDBP is involved in multiple steps of HBV replication via binding to both HBV DNA and RNA. The protein's broad interactome suggests that TARDBP may function as part of a RNA-binding scaffold involved in HBV replication and that the interaction between these proteins might be a target for development of anti-HBV drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Doubly Spliced RNA of Hepatitis B Virus Suppresses Viral Transcription via TATA-Binding Protein and Induces Stress Granule Assembly.J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(22):11406-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00949-15. Epub 2015 Sep 2. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26339052 Free PMC article.
-
SOX2 Represses Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Binding to the Viral EnhII/Cp and Inhibiting the Promoter Activation.Viruses. 2020 Feb 29;12(3):273. doi: 10.3390/v12030273. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32121397 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-26b inhibits hepatitis B virus transcription and replication by targeting the host factor CHORDC1 protein.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 12;289(50):35029-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.589978. Epub 2014 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25342750 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for inhibiting the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in hepatitis B virus.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 7;20(25):7993-8004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.7993. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25009369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Post-transcriptional regulation mechanism and antiviral strategy of hepatitis B virus RNA].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2024 May 20;32(5):474-480. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20240410-00191. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38858198 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis B virus Core protein nuclear interactome identifies SRSF10 as a host RNA-binding protein restricting HBV RNA production.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Nov 12;16(11):e1008593. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008593. eCollection 2020 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 33180834 Free PMC article.
-
Strength in Diversity: Nuclear Export of Viral RNAs.Viruses. 2020 Sep 11;12(9):1014. doi: 10.3390/v12091014. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32932882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hepatitis B Virus Interactome: A Comprehensive Overview.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 16;12:724877. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.724877. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34603251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D signaling inhibits HBV activity by directly targeting the HBV core promoter.J Biol Chem. 2021 Oct;297(4):101233. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101233. Epub 2021 Sep 23. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34562448 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Host Proteins Involved in Hepatitis B Virus Genome Packaging.J Proteome Res. 2024 Sep 6;23(9):4128-4138. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00505. Epub 2024 Jul 30. J Proteome Res. 2024. PMID: 39078123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lavanchy D. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. J. Viral Hepat. 2009;3:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

