Robust estimation of sulcal morphology
- PMID: 31187294
- PMCID: PMC6560124
- DOI: 10.1186/s40708-019-0098-1
Robust estimation of sulcal morphology
Abstract
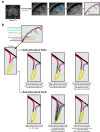
While it is well established that cortical morphology differs in relation to a variety of inter-individual factors, it is often characterized using estimates of volume, thickness, surface area, or gyrification. Here we developed a computational approach for estimating sulcal width and depth that relies on cortical surface reconstructions output by FreeSurfer. While other approaches for estimating sulcal morphology exist, studies often require the use of multiple brain morphology programs that have been shown to differ in their approaches to localize sulcal landmarks, yielding morphological estimates based on inconsistent boundaries. To demonstrate the approach, sulcal morphology was estimated in three large sample of adults across the lifespan, in relation to aging. A fourth sample is additionally used to estimate test-retest reliability of the approach. This toolbox is now made freely available as supplemental to this paper: https://cmadan.github.io/calcSulc/ .
Keywords: Age; Atrophy; Cerebral sulci; Cortical structure; Gyrification; Sulcal depth; Sulcal width.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Lemaitre H, Goldman AL, Sambataro F, Verchinski BA, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR, Mattay VS. Normal age-related brain morphometric changes: nonuniformity across cortical thickness, surface area and gray matter volume? Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33:617.e1–617.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.07.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

