TET2 missense variants in human neoplasia. A proposal of structural and functional classification
- PMID: 31187595
- PMCID: PMC6625141
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.772
TET2 missense variants in human neoplasia. A proposal of structural and functional classification
Abstract
Background: The human TET2 gene plays a pivotal role in the epigenetic regulation of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Somatic TET2 mutations have been repeatedly identified in age-related clonal hematopoiesis and in myeloid neoplasms ranging from acute myeloid leukemia (AML) to myeloproliferative neoplasms. However, there have been no attempts to systematically explore the structural and functional consequences of the hundreds of TET2 missense variants reported to date.
Methods: We have sequenced the TET2 gene in 189 Spanish AML patients using Sanger sequencing and NGS protocols. Next, we performed a thorough bioinformatics analysis of TET2 protein and of the expected impact of all reported TET2 missense variants on protein structure and function, exploiting available structure-and-function information as well as 3D structure prediction tools.
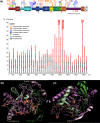
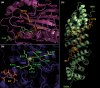
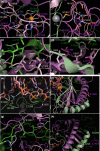
Results: We have identified 38 TET2 allelic variants in the studied patients, including two frequent SNPs: p.G355D (10 cases) and p.I1762V (28 cases). Four of the detected mutations are reported here for the first time: c.122C>T (p.P41L), c.4535C>G (p.A1512G), c.4760A>G (p.D1587G), and c.5087A>T (p.Y1696F). We predict a complex multidomain architecture for the noncatalytic regions of TET2, and in particular the presence of well-conserved α+β globular domains immediately preceding and following the actual catalytic unit. Further, we provide a rigorous interpretation of over 430 missense SNVs that affect the TET2 catalytic domain, and we hypothesize explanations for ~700 additional variants found within the regulatory regions of the protein. Finally, we propose a systematic classification of all missense mutants and SNPs reported to date into three major categories (severe, moderate, and mild), based on their predicted structural and functional impact.
Conclusions: The proposed classification of missense TET2 variants would help to assess their clinical impact on human neoplasia and may guide future structure-and-function investigations of TET family members.
Keywords: 5-methylcytosine; TET2; classification of mutations; epigenetic regulation; neoplasia.
© 2019 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors declare any conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TET2 mutation in acute myeloid leukemia: biology, clinical significance, and therapeutic insights.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Nov 9;16(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01771-2. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39521964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tet oncogene family member 2 gene alterations in childhood acute myeloid leukemia.J Formos Med Assoc. 2016 Sep;115(9):801-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Sep 26. J Formos Med Assoc. 2016. PMID: 26414667
-
TET2 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): results from a comprehensive genetic and clinical analysis of the AML study group.J Clin Oncol. 2012 Apr 20;30(12):1350-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.39.2886. Epub 2012 Mar 19. J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22430270 Clinical Trial.
-
The prognostic impact of tet oncogene family member 2 mutations in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a systematic-review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2019 Apr 25;19(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5602-8. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31023266 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterization of TET1, TET2, and TET3 alterations in myeloid malignancies.Blood. 2009 Jul 2;114(1):144-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-210039. Epub 2009 May 6. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19420352 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Loss of TET2 increases B-1 cell number and IgM production while limiting CDR3 diversity.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 27;15:1380641. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1380641. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38601144 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and interpretation of TET2 noncanonical splicing site intronic variants in myeloid neoplasm patients.EJHaem. 2023 Jun 21;4(3):738-744. doi: 10.1002/jha2.744. eCollection 2023 Aug. EJHaem. 2023. PMID: 37601840 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Implication of DNMT3A and TET2 Genes Mutations in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Dec 1;23(12):4299-4305. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.12.4299. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 36580013 Free PMC article.
-
TET2 mutation in acute myeloid leukemia: biology, clinical significance, and therapeutic insights.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Nov 9;16(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01771-2. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 39521964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TERT and TET2 Genetic Variants Affect Leukocyte Telomere Length and Clinical Outcome in Coronary Artery Disease Patients-A Possible Link to Clonal Hematopoiesis.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 19;10(8):2027. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10082027. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aslanyan, M. G. , Kroeze, L. I. , Langemeijer, S. M. C. , Koorenhof‐Scheele, T. N. , Massop, M. , van Hoogen, P. , … Jansen, J. H. (2014). Clinical and biological impact of TET2 mutations and expression in younger adult AML patients treated within the EORTC/GIMEMA AML‐12 clinical trial. Annals of Hematology, 93(8), 1401–1412. 10.1007/s00277-014-2055-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

