A mutation creating an upstream translation initiation codon in SLC22A5 5'UTR is a frequent cause of primary carnitine deficiency
- PMID: 31187905
- PMCID: PMC6790604
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23839
A mutation creating an upstream translation initiation codon in SLC22A5 5'UTR is a frequent cause of primary carnitine deficiency
Abstract
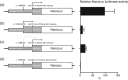
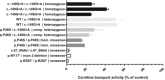
Primary carnitine deficiency is caused by a defect in the active cellular uptake of carnitine by Na+ -dependent organic cation transporter novel 2 (OCTN2). Genetic diagnostic yield for this metabolic disorder has been relatively low, suggesting that disease-causing variants are missed. We Sanger sequenced the 5' untranslated region (UTR) of SLC22A5 in individuals with possible primary carnitine deficiency in whom no or only one mutant allele had been found. We identified a novel 5'-UTR c.-149G>A variant which we characterized by expression studies with reporter constructs in HeLa cells and by carnitine-transport measurements in fibroblasts using a newly developed sensitive assay based on tandem mass spectrometry. This variant, which we identified in 57 of 236 individuals of our cohort, introduces a functional upstream out-of-frame translation initiation codon. We show that the codon suppresses translation from the wild-type ATG of SLC22A5, resulting in reduced OCTN2 protein levels and concomitantly lower transport activity. With an allele frequency of 24.2% the c.-149G>A variant is the most frequent cause of primary carnitine deficiency in our cohort and may explain other reported cases with an incomplete genetic diagnosis. Individuals carrying this variant should be clinically re-evaluated and monitored to determine if this variant has clinical consequences.
Keywords: 5′-untranslated region; OCTN2 deficiency; carnitine transport; primary or systemic carnitine deficiency.
© 2019 The Authors. Human Mutation Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Carnitine uptake defect due to a 5'UTR mutation in a pedigree with false positives and false negatives on Newborn screening.Mol Genet Metab. 2020 Mar;129(3):213-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2019.12.006. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Mol Genet Metab. 2020. PMID: 31864849
-
Functional and molecular studies in primary carnitine deficiency.Hum Mutat. 2017 Dec;38(12):1684-1699. doi: 10.1002/humu.23315. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Hum Mutat. 2017. PMID: 28841266 Free PMC article.
-
[Newborn screening for primary carnitine deficiency and variant spectrum of SLC22A5 gene in Guangzhou].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jun 2;58(6):476-481. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20200323-00292. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32521959 Chinese.
-
Primary Carnitine Deficiency and Newborn Screening for Disorders of the Carnitine Cycle.Ann Nutr Metab. 2016;68 Suppl 3:5-9. doi: 10.1159/000448321. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Ann Nutr Metab. 2016. PMID: 27931018 Review.
-
[Carnitine - mitochondria and beyond].Postepy Biochem. 2016;62(2):85-93. Postepy Biochem. 2016. PMID: 28132459 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Primary carnitine deficiency in two sisters with intractable epilepsy and reversible metabolic cardiomyopathy: Two case reports.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Nov;20(5):118. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9246. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 33005244 Free PMC article.
-
Newborn screening for carnitine transporter defect in Bavaria and the long-term follow-up of the identified newborns and mothers: Assessing the benefit and possible harm based on 19 ½ years of experience.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021 Jun 12;28:100776. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2021.100776. eCollection 2021 Sep. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021. PMID: 34178604 Free PMC article.
-
The global prevalence and genetic spectrum of primary carnitine deficiency.BMC Genom Data. 2025 Jul 7;26(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12863-025-01336-z. BMC Genom Data. 2025. PMID: 40624458 Free PMC article.
-
Mendelian inheritance revisited: dominance and recessiveness in medical genetics.Nat Rev Genet. 2023 Jul;24(7):442-463. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00574-0. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Nat Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 36806206 Review.
-
Intronic variants in inborn errors of metabolism: Beyond the exome.Front Genet. 2022 Dec 6;13:1031495. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1031495. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36561316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Falkenberg, K. D. , Braverman, N. E. , Moser, A. B. , Steinberg, S. J. , Klouwer, F. C. C. , Schluter, A. , … Waterham, H. R. (2017). Allelic expression imbalance promoting a mutant PEX6 allele causes Zellweger spectrum disorder. American Journal of Human Genetics, 101(6), 965–976. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.11.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

