Proresolving Lipid Mediators and Receptors in Stem Cell Biology: Concise Review
- PMID: 31187940
- PMCID: PMC6766599
- DOI: 10.1002/sctm.19-0078
Proresolving Lipid Mediators and Receptors in Stem Cell Biology: Concise Review
Abstract
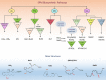
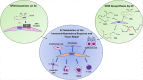
Accumulating evidence indicates that stem cells (SCs) possess immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and prohealing properties. The mechanisms underlying these functions are being investigated with the final goal to set a solid background for the clinical use of SCs and/or their derivatives. Specialized proresolving lipid mediators (SPMs) are small lipids formed by the enzymatic metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids. They represent a leading class of molecules that actively and timely regulate the resolution of inflammation and promote tissue/organ repair. SC formation of these mediators as well as expression of their receptors has been recently reported, suggesting that SPMs may be involved in the immunomodulatory, proresolving functions of SCs. In the present review, we summarize the current knowledge on SPMs in SCs, focusing on biosynthetic pathways, receptors, and bioactions, with the intent to provide an integrated view of SPM impact on SC biology. Stem Cells Translational Medicine 2019;8:992-998.
© 2019 The Authors. Stem Cells Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human Periodontal Stem Cells Release Specialized Proresolving Mediators and Carry Immunomodulatory and Prohealing Properties Regulated by Lipoxins.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Jan;5(1):20-32. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0163. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 26607175 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin A1 and specialized proresolving lipid mediators: promoting resolution as a therapeutic strategy in human inflammatory diseases.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Sep;21(9):879-896. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1364363. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28786708 Review.
-
The Role of Endogenous Specialized Proresolving Mediators in Mast Cells and Their Involvement in Inflammation and Resolution.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 11;26(4):1491. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041491. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Endogenous Proresolving Molecules:Essential Fatty Acid-Derived and Gaseous Mediators in the Resolution of Inflammation.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2016 Jun 1;23(6):655-64. doi: 10.5551/jat.33928. Epub 2016 Apr 6. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2016. PMID: 27052783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro resolving inflammatory effects of the lipid mediators of omega 3 fatty acids and its implication in SARS COVID-19.Med Hypotheses. 2020 Dec;145:110340. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110340. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 33069094 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Could Arachidonic Acid-Derived Pro-Resolving Mediators Be a New Therapeutic Strategy for Asthma Therapy?Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 9;11:580598. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.580598. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33362766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes mellitus promotes susceptibility to periodontitis-novel insight into the molecular mechanisms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 16;14:1192625. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1192625. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37664859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sustained neuronal viability by paracrine factors: new opportunities for endothelial progenitor cell secretome.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Jul;16(7):1429-1430. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.301007. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33318440 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Specialized pro-resolving mediators as modulators of immune responses.Semin Immunol. 2022 Jan;59:101605. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2022.101605. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Semin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35660338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolvin E1 and calvarial defects in rats: a comprehensive histological analysis.Saudi Dent J. 2025 Apr 14;37(1-3):2. doi: 10.1007/s44445-025-00003-4. Saudi Dent J. 2025. PMID: 40397041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Munir H, Ward LSC, Mcgettrick HM. Mesenchymal stem cells as endogenous regulators of inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol 2018;1060:73–98. - PubMed
-
- Sugimoto MA, Vago JP, Perretti M et al. Mediators of the resolution of the inflammatory response. Trends Immunol 2019;40:212–227. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN, Hamberg M, Samuelsson B. Trihydroxytetraenes: A novel series of compounds formed from arachidonic acid in human leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1984;118:943–949. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

