Development of a Zebrafish S1500+ Sentinel Gene Set for High-Throughput Transcriptomics
- PMID: 31188086
- PMCID: PMC6685209
- DOI: 10.1089/zeb.2018.1720
Development of a Zebrafish S1500+ Sentinel Gene Set for High-Throughput Transcriptomics
Abstract
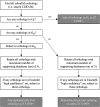
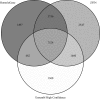
Sentinel gene sets have been developed with the purpose of maximizing the information from targeted transcriptomic platforms. We recently described the development of an S1500+ sentinel gene set, which was built for the human transcriptome, utilizing a data- and knowledge-driven hybrid approach to select a small subset of genes that optimally capture transcriptional diversity, correlation with other genes based on large-scale expression profiling, and known pathway annotation within the human genome. While this detailed bioinformatics approach for gene selection can in principle be applied to other species, the reliability of the resulting gene set depends on availability of a large body of transcriptomics data. For the model organism zebrafish, we aimed to create a similar sentinel gene set (Zf S1500+ gene set); however, there is insufficient standardized expression data in the public domain to train the gene correlation model. Therefore, our strategy was to use human-zebrafish ortholog mapping of the human S1500+ genes and nominations from experts in the zebrafish scientific community. In this study, we present the bioinformatics curation and refinement process to produce the final Zf S1500+ gene set, explore whole transcriptome extrapolation using this gene set, and assess pathway-level inference. This gene set will add value to targeted high-throughput transcriptomics in zebrafish for toxicogenomic screening and other research domains.
Keywords: S1500; S1500+; transcriptomics; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
Co-author P.J.S. is a current employee of BioSpyder Technologies, Inc., which develops and commercializes the TempO-Seq assay for the S1500+ platforms. This commercial affiliation does not alter our adherence to Zebrafish policies and guidelines. All other authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A hybrid gene selection approach to create the S1500+ targeted gene sets for use in high-throughput transcriptomics.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 20;13(2):e0191105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191105. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29462216 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Extrapolating Human S1500+ Genes to the Whole Transcriptome: Tunicamycin Case Study.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2020 Sep 29;14:1177932220952742. doi: 10.1177/1177932220952742. eCollection 2020. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2020. PMID: 33088175 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and advances for transcriptome assembly in non-model species.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 20;12(9):e0185020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185020. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28931057 Free PMC article.
-
Using R and Bioconductor in Clinical Genomics and Transcriptomics.J Mol Diagn. 2020 Jan;22(1):3-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2019.08.006. Epub 2019 Oct 9. J Mol Diagn. 2020. PMID: 31605800 Review.
-
Computational solutions for spatial transcriptomics.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Sep 1;20:4870-4884. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.08.043. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36147664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Translational Toxicology in Zebrafish.Curr Opin Toxicol. 2020 Oct-Dec;23-24:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cotox.2020.05.004. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Curr Opin Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32656393 Free PMC article.
-
Toward Sustainable Environmental Quality: Priority Research Questions for Asia.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2020 Aug;39(8):1485-1505. doi: 10.1002/etc.4788. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32474951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput gene expression analysis with TempO-LINC sensitively resolves complex brain, lung and kidney heterogeneity at single-cell resolution.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31285. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82736-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39732835 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic workflows for deriving transcriptomic points of departure: current status, data gaps, and research priorities.Toxicol Sci. 2025 Feb 1;203(2):147-159. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae145. Toxicol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39499193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in toxicogenomics to protect human health.Nat Rev Genet. 2025 Feb;26(2):105-122. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00767-1. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Nat Rev Genet. 2025. PMID: 39223311 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
