Genome-wide identification and characterization of R2R3-MYB genes in Medicago truncatula
- PMID: 31188936
- PMCID: PMC6905446
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2018-0235
Genome-wide identification and characterization of R2R3-MYB genes in Medicago truncatula
Abstract
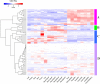
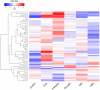
MYB is a large family of plant transcription factors. Its function has been identified in several plants, while there are few reports in Medicago truncatula. In this study, we used RNA-seq data to analyze and identify R2R3-MYB genes in the genome of Medicago truncatula. Phylogenetic analysis classified 150 MtMYB genes into 21 subfamilies with homologs. Out of the 150 MtMYB genes, 139 were distributed among 8 chromosomes, with tandem duplications (TD) and segment duplications (SD). Microarray data were used for functional analysis of the MtMYB genes during growth and developmental processes providing evidence for a role in tissues differentiation, seed development processes, and especially the nodulation process. Furthermore, we investigated the expression of MtMYB genes in response to abiotic stresses using RNA-seq data, which confirmed the critical roles in signal transduction and regulation processes under abiotic stress. We used quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) to validate expression profiles. The expression pattern of M. truncatula MYB genes under different abiotic stress conditions suggest that some may play a major role in cross-talk among different signal transduction pathways in response to abiotic stresses. Our study will serve as a foundation for future research into the molecular function of M. truncatula R2R3-MYB genes.
Figures




References
-
- Al-Attala MN, Wang X, Abou-Attia MA, Duan X, Kang Z. A novel TaMYB4 transcription factor involved in the defence response against Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici and abiotic stresses. Plant Mol Biol. 2014;84:589–603. - PubMed
-
- Benedito VA, Torres-Jerez I, Murray JD, Andriankaja A, Allen S, Kakar K, Wandrey M, Verdier J, Zuber H, Ott T, et al. A gene expression atlas of the model legume Medicago truncatula . Plant J. 2008;55:504–513. - PubMed
-
- Chen BJ, Wang Y, Hu YL, Wu Q, Pin ZP. Cloning and characterization of a drought inducible MYB gene from Boea crassifolia . Plant Sci. 2005;168:493–500.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

