Evaluation of QoL in neurofibromatosis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis study
- PMID: 31189476
- PMCID: PMC6560778
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-019-1338-y
Evaluation of QoL in neurofibromatosis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis study
Abstract
Background: The neurofibromatoses (NF) are a group of genetic disorders that interfere negatively with the quality of life (QoL) and influence physical, emotional and social statuses. Studying the effects of neurofibromatoses on various aspects of QoL seems important to implement beneficial strategies in increasing the QoL of NF patients. The aim of this study was to review the literature on quality of life in patients with NF and quantitatively evaluate the effects of Neurofibromatosis on various aspects of quality of life by synthesizing available studies.
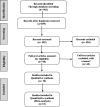
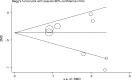
Methods: This article is written according to the PRISMA checklist. Different databases including PubMed, Scopus, Google scholar and Web of Science were searched to identify studies that examined QoL of patients with neurofibromatosis. The relevant data obtained from these papers were analyzed by a random-effects model. The heterogeneity of studies was calculated using the I2 index and Egger test was used to determine publication bias. The information was analyzed by R and STATA Ver 14.
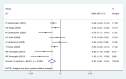
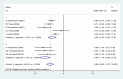
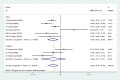
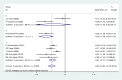
Results: Twelve studies were selected as eligible for this research and were included in the final analysis. The number of participants in the study was 7314 individuals containing 910 NF patients (642 NF1 and 268 NF2) and 6404 healthy subjects. The mean scores of sub-scales of QoL were significantly lower in NF patients compared with control except for the scale of cohesion. Family and NF patients had lower quality of life in all aspects of QoL than controls. Also, this meta-analysis shows that NF negatively effects on physical function, bodily pain, mental health, social function and general health. Subgroup analysis showed that NF had negative effects on all sub-scales of QoL if the study was conducted in adults and used a SF-36 questionnaire.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis suggests that NF is a broad spectrum disease, affecting physical function, bodily pain, mental health, social function and general health.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; Neurofibromatosis; Quality of life; Schwannomatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lu-Emerson C, Plotkin SR. The neurofibromatoses. Part 1: NF1. Rev Neurol Dis. 2009;6:47–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

