The gut microbiota regulates white adipose tissue inflammation and obesity via a family of microRNAs
- PMID: 31189717
- PMCID: PMC7050429
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav1892
The gut microbiota regulates white adipose tissue inflammation and obesity via a family of microRNAs
Abstract
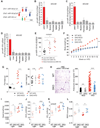
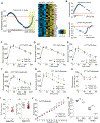
The gut microbiota is a key environmental determinant of mammalian metabolism. Regulation of white adipose tissue (WAT) by the gut microbiota is a process critical to maintaining metabolic fitness, and gut dysbiosis can contribute to the development of obesity and insulin resistance (IR). However, how the gut microbiota regulates WAT function remains largely unknown. Here, we show that tryptophan-derived metabolites produced by the gut microbiota controlled the expression of the miR-181 family in white adipocytes in mice to regulate energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity. Moreover, dysregulation of the gut microbiota-miR-181 axis was required for the development of obesity, IR, and WAT inflammation in mice. Our results indicate that regulation of miR-181 in WAT by gut microbiota-derived metabolites is a central mechanism by which host metabolism is tuned in response to dietary and environmental changes. As we also found that MIR-181 expression in WAT and the plasma abundance of tryptophan-derived metabolites were dysregulated in a cohort of obese human children, the MIR-181 family may represent a potential therapeutic target to modulate WAT function in the context of obesity.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
E.J.W. has consulting agreements with and is on the scientific advisory boards for Merck, Roche, Pieris, Elstar, and Surface Oncology. E.J.W. has a patent licensing agreement on the PD-1 pathway with Roche/Genentech: “Methods and Compositions for the treatment of persistent infections and cancer by inhibiting the programmed cell death (PD-1) pathway”, US patent number 14/144,304. S. E. H. has advised for Horizon Pharma.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 AI124538/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007356/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI117950/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI128060/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082630/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK122677/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI135091/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD043245/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI108545/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI105343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK111755/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD043021/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007780/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA210944/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DK094708/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI055428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI070077/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HL138739/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136572/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

