Framing effect, probability distortion, and gambling tendency without feedback are resistant to two nights of experimental sleep restriction
- PMID: 31189964
- PMCID: PMC6561965
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-44237-9
Framing effect, probability distortion, and gambling tendency without feedback are resistant to two nights of experimental sleep restriction
Abstract
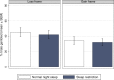
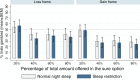
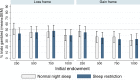
Several studies suggest that sleep deprivation affects risky decision making. However, most of these are confounded by feedback given after each decision, indicating that decisions may be based on suboptimal feedback-learning rather than risk evaluation. Furthermore, few studies have investigated the effect of sleep loss on aspects of prospect theory, specifically the framing effect and probability distortion. In this within-subjects design, 25 people had (i) two nights of an 8 h sleep opportunity, and (ii) two nights of a 4 h sleep opportunity, in a counter-balanced order. Following the two nights, they performed a gambling task with no immediate feedback; for each round, they could either gamble for a full amount, or take a settlement framed as a gain or a loss for part of the amount. Sleep restriction did not significantly affect the tendency to gamble, the framing effect, or probability distortion, as compared to normal sleep. These results indicate that two nights of sleep restriction affects neither general gambling tendency, nor two of the main predictions of prospect theory. This resilience may be due to a less extreme sleep loss than in previous studies, but also indicates that learning components and risk biases should be separated when assessing the effect of sleep loss on risky behaviour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Feedback Blunting: Total Sleep Deprivation Impairs Decision Making that Requires Updating Based on Feedback.Sleep. 2015 May 1;38(5):745-54. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4668. Sleep. 2015. PMID: 25515105 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impaired decision making following 49 h of sleep deprivation.J Sleep Res. 2006 Mar;15(1):7-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2869.2006.00487.x. J Sleep Res. 2006. PMID: 16489997
-
Does insufficient sleep affect how you learn from reward or punishment? Reinforcement learning after 2 nights of sleep restriction.J Sleep Res. 2021 Aug;30(4):e13236. doi: 10.1111/jsr.13236. Epub 2020 Nov 20. J Sleep Res. 2021. PMID: 33219629 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep deprivation elevates expectation of gains and attenuates response to losses following risky decisions.Sleep. 2007 May;30(5):603-9. doi: 10.1093/sleep/30.5.603. Sleep. 2007. PMID: 17552375
-
The effects of sleep deprivation on risky decision making.Psychon Bull Rev. 2025 Feb;32(1):80-96. doi: 10.3758/s13423-024-02549-6. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Psychon Bull Rev. 2025. PMID: 39080188 Review.
Cited by
-
Keep your budget together! Investigating determinants on risky decision-making about losses.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 21;17(3):e0265822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265822. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35312723 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep Deprivation Impairs Cooperative Behavior Selectively: Evidence from Prisoner's and Chicken Dilemmas.Nat Sci Sleep. 2020 Jan 20;12:29-37. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S237402. eCollection 2020. Nat Sci Sleep. 2020. PMID: 32021522 Free PMC article.
-
Sex moderates the effects of total sleep deprivation and sleep restriction on risk preference.Sleep. 2022 Sep 8;45(9):zsac120. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsac120. Sleep. 2022. PMID: 35667000 Free PMC article.
-
Training in statistical analysis reduces the framing effect among medical students and residents in Argentina.J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2020;17:25. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2020.17.25. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2020. PMID: 32867406 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of total sleep deprivation and related mood changes on approach-avoidance decisions to threat-related facial displays.Sleep. 2021 Dec 10;44(12):zsab186. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsab186. Sleep. 2021. PMID: 34313789 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

